
A Global Capability Centre (GCC) is no longer a back office. It represents a global technology hub, which owns products and is an engine of innovation and anchors the strategic functions of multinational enterprises. Approximately 1.9 million professionals work in India’s 1,900 GCCs, which are now producing billions of dollars in revenue and shifting to high-value engineering, artificial intelligence, analytics, and product ownership. It seems that GCC requires a new skill base compared to what traditional captive centres used to provide 10 years ago. The blog outlines the skills that can ensure a professional succeeds within a GCC, why these skills are important to employers and provides a concise and practical roadmap to people preparing to work at a GCC company. GCCs will require this futuristic tone as they expand from intellectual property and product leadership to capability arbitrage.
GCCs currently play a direct role in national output and competitiveness in export; analysts have estimated that direct GCC output has consistently been increasing by double-digit CAGR and is expected to grow vigorously by 2030. GCCs provide business impact through economic benefits such as talent specialisation, reduced time to market for global products, and low-cost innovation, and these centres have become R&D and AI hubs. Innovative investments and business decisions to have strategic engineering and information functions in India are clear examples of this competency transformation.
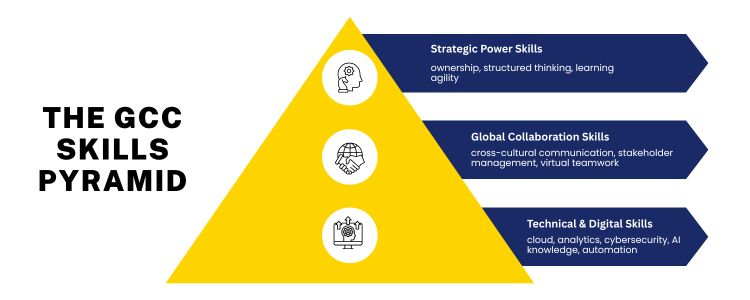
There are five complementary skills that successful GCC professionals possess:
1. Technical and Digital Skills For GCC These are the technical Gcc Roles skills, which assist product engineering and digital transformation. The surveys on GCC recently show that the proportion of centres that invest in AI and automation teams as a core capability is rising. 2. Business & Domain Knowledge 3. International Customer Relationship Management and International Communication. 4. Design Thinking and Problem Solving 5. Power Skills
Anticipate GCCs to increase the pace of investment in agentic AI, model governance, data fabrics and embedded security. There will be a huge demand for T-shaped professionals who are well-versed in their field and have connections to business, communication, and tooling. New centres are also being established by GCCs in new cities in India, which is driving up regional engineering talent demand and forming pockets of opportunity outside of metros.
Global Capability Centres will remain to play the role of global technology centres and innovation hubs. Professionals have an easy road ahead of them: develop technical depth and business perspective, hone global communication skills, and increase flexibility. That is the key to valuable, future-proof careers in the GCCs, as well as the strategic economic benefits that the GCCs will bring to India and global companies that choose to invest in India. Recent business news and business real estate predictions verify the pattern: GCCs are investing in high value ability and hiring skill sets which can deliver strategic results, rather than cost reduction.
Hyderabad, Bangalore and Pune have become significant pharma innovation centres with global delivery centres of major biotechnological and pharmaceutical firms such as Novartis, Pfizer, AstraZeneca and GSK. They offer an economic benefit of calculation, a variety of scientific and technical human resources, and speedy time-to-market. On average, businesses reduce between 25-40 percent of the operational costs and increase the rate of innovation. The next-generation operations of Pharma GCC focus on advanced molecular modelling, AI/ML-based drug discovery, cloud supercomputing, and data integration platforms, as well as quantum-ready simulations. Pharma GCCs use AI to screen molecules, predict the efficacy of drugs, optimise clinical trials and aid in making data-driven decisions, resulting in smarter, faster and safer drug pipelines. Pharma GCCs will be global innovation ecosystems that are a combination of computational chemistry, generative AI, and quantum computing. They will turn into the hubs linking data science, discovery and regulatory intelligence in the global arena. Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.
Why GCC Value Drivers Are Skills Rather Than Degrees.
The Contemporary Global Capability Centers Skills Formula
Core Skill Areas
Skills by Function
GCC Function
Typical Skills Required
Data & Analytics
SQL, Python, statistics, BI dashboards
Cloud & Infrastructure
Cloud architecture, IaC, monitoring
Product Engineering
System design, agile, CI/CD, testing
Cybersecurity
Security requirements, policy, threat modelling, and secure coding.
Finance & Risk
FP&A, regulatory reporting, data modelling
HR & Talent CoE
HR analytics, learning design, change management
Short-Term Projection (2025–2030)
A Road Map for Candidates
Conclusion
frequently asked questions (FAQs)

Aditi
Hey, like this? Why not share it with a buddy?
Related Posts
Recent Blog / Post
- Pharma GCC Setup Services in India: Strategic Considerations for CXOs January 9, 2026
- Why Enterprises Are Rethinking Their GCC Strategies in 2026 January 8, 2026
- Why Most Enterprise Expansion Strategies Fall Short of Projections, And How a GCC Enabler Can Bridge the Gap January 7, 2026
- India’s GCC Ecosystem: Why the World’s Biggest Companies Are Betting Their Future on it January 3, 2026
- Healthcare GCCs in India: Where the World’s Pharmaceutical Innovation Actually Happens January 2, 2026
- Circular Economy Models and Their Relevance to Manufacturing GCCs December 30, 2025
- GCCs in Agritech: Digitizing Global Food Security December 29, 2025
- Renewable Energy GCCs: Accelerating Global Green-Tech Development December 29, 2025
- Cyber Resilience 2030: Multi-Layer Security Architecture for GCCs December 26, 2025
- Building an Integrated Risk Management Framework for Multi-Region GCCs December 26, 2025
- The Ethics of Automation: How GCCs Maintain Human Oversight in AI Workflows December 25, 2025
- Future of HR in GCCs: Data-Led, Skills-Based, and GenAI-Driven December 25, 2025
- The Proposal to Standardize India’s GCCs for Unshakeable Global Leadership December 24, 2025
- Global Capability Centers: A Strategic Growth Model for B2B Enterprises December 24, 2025
- AI Ethics & Compliance Mandates for GCC Operations in 2025 December 23, 2025
















