
The Global Capability Centres (GCCs) of India have developed beyond cost-arbitrage service delivery centers to become strategic, pioneering hubs that develop solutions in India and export them worldwide. There are currently more than 1,900 GCCs operating in India, which produced approximately 64.6 billion in revenues and hired approximately 1.9 million professionals, signalling clearly that MNC GCCs in India have become drivers of cross-border innovation. In this blog, 10 acute reverse-innovation success stories are shared, along with the reason why India is a good place to innovate in emerging markets, the economic benefits of innovation and the near future of global impact led by the GCC. GCCs in India are expected to grow even more, and market size is expected to grow to up to $99-105 billion as centres progress up the value chain to product engineering, AI, and sustainability platforms. This expansion supports a structural change: Indian GCCs do not only execute processes; they also develop global products and global business models that address issues or challenges, initially developed in India but adapted to the global market.
All of these factors together make India an experimental “lab” to scale internationally.
Assume GCCs will lead in reverse innovation around GenAI uses, sustainable consumer products, frugal health technology, and urban mobility. As market size is expected to reach close to 100B in 2030, MNC GCCs in India will take center stage in the product roadmaps and global competitiveness of parent firms.
The MNC GCCs in India stopped being cost centres; they are now innovation exporters. To leaders and policymakers in the enterprise, the task is straightforward: invest in GCC ecosystems, create cross-sector partnerships, and form incentive mechanisms that translate India-first ideas into global products. Indian GCCs will find themselves increasingly sought after as the world finds a scalable solution to some of the most demanding markets in the world.
A GDC refers to a single-minded offshore deployment, which provides proficient business, technology and operational services to corporate bodies on a global basis. BFSI, IT services, healthcare, telecom, retail, manufacturing, and other upcoming technologies, including AI and blockchain. They do not only target cost savings but now aim at innovation, automation, R&D, digital transformation, and high-value consulting. They design and create cloud, artificial intelligence, analytics, cloud security, and process automation. A large supply of STEM graduates, multilingual workers and niche skills in AI, ML, cloud, and analytics. Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.
10 Reverse-Innovation Success Stories
MNC (India GCC)
Innovation (Made in India)
India-Origin Context
Global Impact
GE Healthcare (Bengaluru)
Low-cost portable ECG & diagnostics
Developed for rural Indian hospitals with limited electricity and trained staff
Adopted in emerging markets across Africa, Southeast Asia, and eventually in telehealth programs in the US
Microsoft (Hyderabad)
AI-driven accessibility tools (low-bandwidth, voice-enabled)
Designed for India’s heterogeneous linguistic and connectivity landscape
Integrated globally into Microsoft’s accessibility suite, helping users in Europe, Africa, and the Americas
Walmart Global Tech (Bengaluru)
AI demand forecasting for small-store supply chains
Created for India’s fragmented retail ecosystem with thousands of small kirana stores
Scaled to optimise Walmart supply chains in the US, LATAM, and Africa
Abbott India (R&D Hub)
Affordable point-of-care diagnostic kits
Innovated for rural Indian clinics needing cost-effective testing
Distributed in Southeast Asia and Africa and used in emerging-market global initiatives
Unilever (Bengaluru)
Consumer insights platform leveraging mobile data & local buying patterns
Developed for India’s diverse consumer base to track micro-trends
Platform now informs product launches and marketing in Europe, the US, and Asia-Pacific.
Nissan Digital Hub (Trivandrum)
Compact connected-car telematics for congested cities
Designed for high-density urban Indian traffic conditions
Applied in Europe and Asia for smart city mobility solutions
JPMorgan Chase (Mumbai)
AI-powered risk analytics & predictive models
Built using Indian market transactional data for high-frequency trading and compliance
Rolled out to global trading desks and risk units in New York, London, and Singapore
Bosch India (Bengaluru)
Low-cost IoT modules for smart appliances
Developed for Indian households seeking energy-efficient devices at lower price points
Integrated into Bosch’s global smart home and industrial IoT portfolio
PepsiCo (Gurgaon)
Sustainable, affordable packaging solutions
Innovated to reduce packaging cost and environmental impact in India
Adopted in global operations to reduce waste and improve sustainability metrics
SAP Labs India (Bengaluru)
Embedded sustainability analytics & reporting tools
Built to meet India’s regulatory reporting and ESG compliance needs
Now core to SAP’s global SaaS offering for multinational clients
Major Observations of the Following Stories:
Why is India a Leader in Reverse Innovation?
Economic Benefits
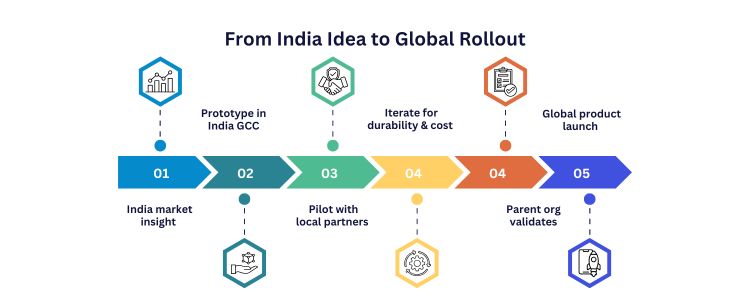
Future Outlook
Conclusion
frequently asked questions (FAQs)

Aditi
Hey, like this? Why not share it with a buddy?
Related Posts
Recent Blog / Post
- Why Mid-Sized Companies are Embracing the GCC Model October 16, 2025
- What Is A Global Capability Center (GCC), and Why Is It Essential For Modern Business? October 16, 2025
- Gurugram’s Tech Ascent: Decoding the New Haryana GCC Policy October 15, 2025
- Scaling Your Tech Team: A Beginner’s Look at the Offshore Development Center October 15, 2025
- Agile Methodologies for GCCs: A Blueprint for Success October 6, 2025
- The Legal and Compliance Checklist for a New GCC Setup October 4, 2025
- The Rise of Niche GCCs: A Focus on Specialised Capabilities October 4, 2025
- The Impact of Regulatory Changes on GCC Operations October 4, 2025
- Cybersecurity for GCCs: A Proactive Approach to Data Protection September 30, 2025
- Beyond Cost: Measuring the True ROI of Your GCC Investment September 29, 2025
- The Future of GCCs in the Retail Sector: A Strategic Playbook September 29, 2025
- David vs Goliath: Mid-Sized GCCs Quietly Outperform the Big Brands September 29, 2025
- Infineon’s Big Bet on India: Inside Its First GCC in GIFT City September 29, 2025
- From Campuses to Capability Centres: How Indian Universities Power the Global GCC Ecosystem September 29, 2025
- Retail Meets Digital: Costco’s GCC in Hyderabad Marks a Global Shift September 29, 2025
















