
The last mile of an engineering and innovation process is the visible convenience when a customer in Lagos taps open a digital wallet and sees an instant loan decision, or when a rural merchant in Andhra Pradesh scans a tap-to-pay UPI QR and the payment is sent in a matter of seconds. That is being mapped increasingly within Global Capability Centres (GCCs), strategic centres which integrate engineering, data science, product design and regulatory expertise to drive the fintech and digital banking megawave.
The fintech market is accelerating: industry projections project the global fintech market to be USD 340-395 billion in 2024-25 and expect further double-digit CAGR in the second half of the decade. India has established itself as the GCC powerhouse with approximately 1,900 GCCs, which provide approximately two million individuals with jobs and 64-65 billion dollars in revenue. This places India as a hub of the engineering base of global financial services transformation. Similarly, digital rails like India’s UPI have been setting volume records – a measure of the innovation of fintech products in day-to-day economic life.
GCCs started as captive IT and back-office centres based on the cost arbitrage. They have developed into product and research centres in over three technology cycles: the current GCCs have cloud-native engineering, AI laboratories, RegTech units and UX studios that create the customer experiences of the future. This development is of importance to fintech and digital banking, as it is shifting decisions nearer to the teams that are developing features like real-time payments, risk engines and embedded finance.
To support banks in turning into neobanks, launching B2B embedded finance services, and creating modular payments stacks, GCCs create end-to-end digital banking platforms which are cloud-native, API-first, and mobile-first to be launched in shorter timelines than existing BU timelines. The outcome: condensed go-to-market and product experimentation velocity. GCC data teams create predictive credit models, transactional-level fraud detectors and personal recommendation engines. Banks can introduce smarter underwriting and real-time decisioning in various markets with consolidated datasets and ML infrastructure within GCCs. GCCs have SOCs, operational behavioural fraud analytics, and privacy-preserving data archetypes in prototyping. As they are closer to product teams, the feedback loop between secure design and customer experience is less long, which is essential in terms of trust in digital banking. GCCs tend to become transnational sandboxes where product, policy and partner teams pilot integrating open banking, tokenization, and CBDCs, coordinating product strategies to regulatory boundaries across borders. Humanising fintech flows, GCC design focuses on UX research into microinteractions: onboarding, consent screens and recovery journeys that drop off and add to lifetime value. Strategic Impact of GCCs on Fintech & Digital Banking
This is being hastened by policy and technology developments. New statements on biometric authentication of online payments and the widening capabilities of online payments show how the national payments infrastructure is changing: both as an opportunity and an engineering requirement that GCCs must build new authentication, identity and privacy paradigms into products. At the state level, specific GCC policies strive to increase the number of capability centres and employment further, which will indicate the further state support of GCC-based innovation.
Export Earnings and Jobs – GCCs invest in high-value jobs and high-service exports. Looking Forward GCCs will take on roles as Centers of Excellence in GenAI-related personal finance, digital identity solutions, and composable banking platforms over the upcoming 5 years. They will play a central role in bringing embedded finance to non-bank ecosystems, uniting real-time payments with loyalty, commerce, and credit. Winners in the ever-competitive GCC fintech market will be GCCs that incorporate product ownership, regulatory fluency, and cloud economics.
The control room is getting more GCC, and the front door of digital banking is user experience. The GCCs will deliver more than just a code; they will build operational resilience, cross-border scale, trust, and a quicker and safer customer experience. Aligning strategy to the best of the GCC is not an option anymore but the core of the future of finance in the eyes of banks and fintech bootstrappers alike.
A GCC is an offshore facility of a multinational company that undertakes niche roles such as research and development, information technology service and strategic management. It is a government program that gives the women entrepreneurs up to 1 crore in bank loans to fund greenfield projects. Personal responsibilities and unconscious bias are the factors that lead to their mid-career attrition and slow them down in their careers. They introduce new ideas, understanding, and team-oriented leadership that speeds up the advancement of such areas as AI and cybersecurity. By 2030, women are expected to take up 25-30 per cent of GCC leadership positions, which will be paramount to the growth of the Indian market. Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.
Introduction
The Evolution
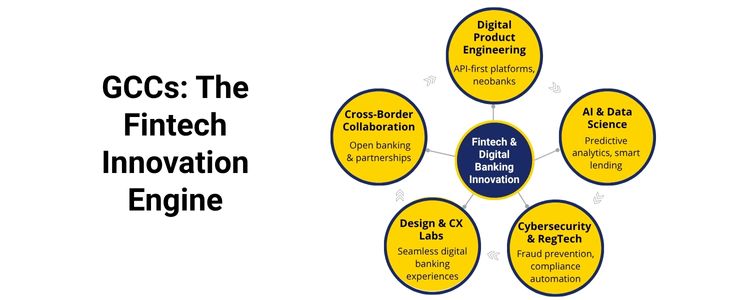
The Playbook To Speed Up Fintech & Digital Banking
Domain
GCC Role
Strategic Benefit
Product Engineering
Build API-first digital banking platforms
Faster launches, modular scaling
AI & Analytics
Predictive credit & fraud models
Lower defaults, better UX
Cybersecurity
Continuous security engineering
Reduced risk, regulatory readiness
Compliance & RegTech
Localized regulatory automation
Faster market entry, lower penalties
UX & CX
Research-led localised design and testing
Higher activation & retention
Existing Events and Policy Tailwinds
Economic Benefits
Conclusion
frequently asked questions (FAQs)

Aditi
Hey, like this? Why not share it with a buddy?
Related Posts
Recent Blog / Post
- Pharma GCC Setup Services in India: Strategic Considerations for CXOs January 9, 2026
- Why Enterprises Are Rethinking Their GCC Strategies in 2026 January 8, 2026
- Why Most Enterprise Expansion Strategies Fall Short of Projections, And How a GCC Enabler Can Bridge the Gap January 7, 2026
- India’s GCC Ecosystem: Why the World’s Biggest Companies Are Betting Their Future on it January 3, 2026
- Healthcare GCCs in India: Where the World’s Pharmaceutical Innovation Actually Happens January 2, 2026
- Circular Economy Models and Their Relevance to Manufacturing GCCs December 30, 2025
- GCCs in Agritech: Digitizing Global Food Security December 29, 2025
- Renewable Energy GCCs: Accelerating Global Green-Tech Development December 29, 2025
- Cyber Resilience 2030: Multi-Layer Security Architecture for GCCs December 26, 2025
- Building an Integrated Risk Management Framework for Multi-Region GCCs December 26, 2025
- The Ethics of Automation: How GCCs Maintain Human Oversight in AI Workflows December 25, 2025
- Future of HR in GCCs: Data-Led, Skills-Based, and GenAI-Driven December 25, 2025
- The Proposal to Standardize India’s GCCs for Unshakeable Global Leadership December 24, 2025
- Global Capability Centers: A Strategic Growth Model for B2B Enterprises December 24, 2025
- AI Ethics & Compliance Mandates for GCC Operations in 2025 December 23, 2025
















