
By 2025, bilateral trade between India and Japan had reached an all-time high of 22.85 billion dollars, with Japanese exports to India and Indian imports reaching 17.69 and 5.16 billion, respectively. This growth underscores the reality that a growing economic relationship is being formed between the two nations. However, there are also other challenges, such as cultural differences and operational challenges. Global Capability Centres (GCCs) have taken center stage as key enablers in eliminating the gaps, a dynamic synergy that creates mutual growth and innovation.
Global Capability Centers also refer to offshore capability centers that are developed by any multinational organisation to consolidate and streamline different business operations such as IT services, research & development, accounting and customer services. These centers were established mainly on the basis of cost arbitrage. Now, they have become strategic centres, which add to innovation, digital transformation and global competitiveness.
Cultural Integration and Operational Alignment The ability to fit perfectly with various international work cultures is becoming a well-acknowledged trait of Indian professionals. Such flexibility has proved a decisive factor in multinational companies either locating or increasing their GCC presence in India. GCCs are the intermediaries, matching Japanese precision and work ethics with Indian agility and innovativeness, thus creating a working atmosphere to enhance business success. Innovation and Technology Transfer GCCs help in exchanging the new technologies and innovative practices between Japan and India. As an example, Japanese enterprises have used GCCs in India to introduce AI-based solutions, facilitate product development cycles, and optimize operations resulting in effectiveness and competitive business practices in the global market. Economic and Strategic Benefits The creation of the GCCs in India is associated with a number of economic benefits, such as lower operational expenses, availability of a competent workforce, and increased scalability. The following advantages are specifically attracting Japanese firms that want to increase their presence worldwide without compromising on cost-efficiency and performance.
GCCs have developed a lot in India, and the number of centers has increased from the estimated 700 centers in 2010 to more than 1,960 in 2025. These centers earned a revenue of US $64.6 billion, and in the financial year 2025 and more than 19 lakh professionals got employment. By 2030, the GCC scenario is estimated to have an annual income of 99 to 108 billion, and more than 2,500 centers are expected to open.
Some industries are pioneers in India-Japan trade coordination, and they are:
The changing role of the GCC in India-Japan trade relations is a sign of change in the direction of a more collaborative partner. With the help of cultural coordination, technological innovations and strategic alliances, the two countries are in a position to conquer the complexities of the global market and achieve long-term economic development. Further development of the GCC will play an important role in realising the capabilities of this lively alliance.
A GDC refers to a single-minded offshore deployment, which provides proficient business, technology and operational services to corporate bodies on a global basis. BFSI, IT services, healthcare, telecom, retail, manufacturing, and other upcoming technologies, including AI and blockchain. They do not only target cost savings but now aim at innovation, automation, R&D, digital transformation, and high-value consulting. They design and create cloud, artificial intelligence, analytics, cloud security, and process automation. A large supply of STEM graduates, multilingual workers and niche skills in AI, ML, cloud, and analytics. Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.
The Global Capability Centres (GCCs)
The Role of GCCs in Indo-Japan Business Synergy
Economic Impact and Development
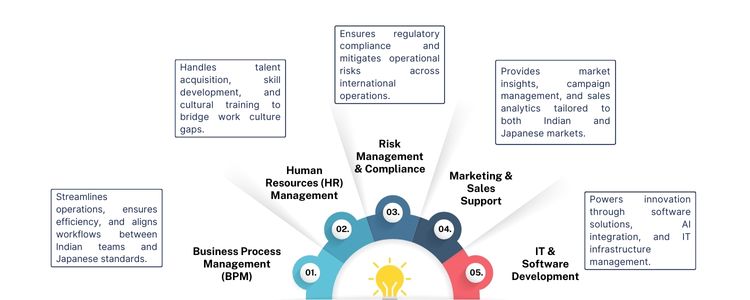
Areas Contributing to India-Japan Coordination.
Key Benefits of GCCs in Indo-Japan Business Synergy
Benefit
Description
Cultural Integration
Facilitates seamless collaboration by aligning work ethics and practices.
Cost Efficiency
Reduces operational expenses through optimised processes and resource utilisation.
Innovation Transfer
Enables the exchange of advanced technologies and innovative practices.
Economic Development
GDP contributes to gross domestic product (GDP) growth through an increase in trade and investment.
Strategic Expansion
Global market expansion is supported by providing measuring and flexible operations.
Conclusion
frequently asked questions (FAQs)

Aditi
Hey, like this? Why not share it with a buddy?
Related Posts
Recent Blog / Post
- Pharma GCC Setup Services in India: Strategic Considerations for CXOs January 9, 2026
- Why Enterprises Are Rethinking Their GCC Strategies in 2026 January 8, 2026
- Why Most Enterprise Expansion Strategies Fall Short of Projections, And How a GCC Enabler Can Bridge the Gap January 7, 2026
- India’s GCC Ecosystem: Why the World’s Biggest Companies Are Betting Their Future on it January 3, 2026
- Healthcare GCCs in India: Where the World’s Pharmaceutical Innovation Actually Happens January 2, 2026
- Circular Economy Models and Their Relevance to Manufacturing GCCs December 30, 2025
- GCCs in Agritech: Digitizing Global Food Security December 29, 2025
- Renewable Energy GCCs: Accelerating Global Green-Tech Development December 29, 2025
- Cyber Resilience 2030: Multi-Layer Security Architecture for GCCs December 26, 2025
- Building an Integrated Risk Management Framework for Multi-Region GCCs December 26, 2025
- The Ethics of Automation: How GCCs Maintain Human Oversight in AI Workflows December 25, 2025
- Future of HR in GCCs: Data-Led, Skills-Based, and GenAI-Driven December 25, 2025
- The Proposal to Standardize India’s GCCs for Unshakeable Global Leadership December 24, 2025
- Global Capability Centers: A Strategic Growth Model for B2B Enterprises December 24, 2025
- AI Ethics & Compliance Mandates for GCC Operations in 2025 December 23, 2025
















