
The market in Global Capability Centre (GCC) services is projected to grow to 403.22 billion in 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.21 percent. This development highlights the strategic change from the conventional offshore delivery modes to the advanced, multi-location worldwide hub networks. Businesses are also forming integrated centers in different geographies in order to become resilient, innovative and efficient in operations.
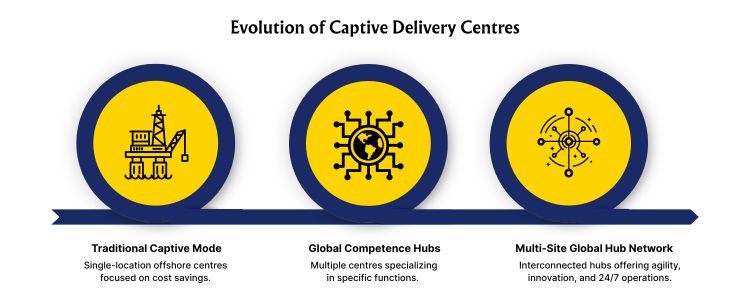
The main reason behind the creation of Captive Delivery Centres was the cost arbitrage and process control. But with the changing dynamics of global business, the role of these centers changed as well. The development may be outlined in three phases:
Multi-location worldwide hub network possesses several strategic benefits: Business Continuity and Risk Mitigation: Distributed operations across the geographical locations aid in reducing the geopolitical tensions, natural calamities, or economic recession within a particular state. Presence of Diverse pool of talent: The different countries are typified by different talents. As an example, Eastern Europe can provide experience in the area of cybersecurity, and Southeast Asia can provide software development. More Innovation and Knowledge Sharing: Interconnected hubs facilitate sharing of ideas and best practices that result in the creation of a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. Operational Efficiency: The network can be integrated to ensure that 24 hours a day work is done to ensure maximum productivity and that the time to market of the products and services is minimized.
To design and establish a multi-site global hub network in the most effective manner, organizations require the following strategic pillars to do so:
There is a great economic implication to the growth of GCCs. In India, e.g., the GCC industry is estimated to expand from 64.6 billion in 2024 to 110 billion in 2030, and the number of centers will grow to 3500 in 2030. This has been facilitated by the following factors: In the future, the work of GCCs is likely to be transformed, and an increased focus on the digital transformation, artificial intelligence, and sustainable business is likely to be implemented. Such changes will require organizations to adjust to the new environment by adopting new technologies, a spirit of lifelong learning, and dynamic approaches that may enable them to react to the dynamic global business environment.
One of the biggest shifts in how businesses operate internationally is the replacement of traditional captive delivery centres with sophisticated multi-site global networks of hubs. Business organisations can create and implement networked hubs to be resilient, innovative, and operationally excellent. Businesses that want to remain competitive and contribute to the increasingly complex and interconnected world must embrace this model because the business world is always evolving.
A GCC is an offshore facility of a multinational company that undertakes niche roles such as research and development, information technology service and strategic management. It is a government program that gives the women entrepreneurs up to 1 crore in bank loans to fund greenfield projects. Personal responsibilities and unconscious bias are the factors that lead to their mid-career attrition and slow them down in their careers. They introduce new ideas, understanding, and team-oriented leadership that speeds up the advancement of such areas as AI and cybersecurity. By 2030, women are expected to take up 25-30 per cent of GCC leadership positions, which will be paramount to the growth of the Indian market. Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.
Development Of The Captive Delivery Centres.
Multi-Site Hub Network Strategic Advantages
Designing a Multi-Site Global Hub Network.
Economic Effects
Conclusion

frequently asked questions (FAQs)

Aditi
Hey, like this? Why not share it with a buddy?
Related Posts
Recent Blog / Post
- Pharma GCC Setup Services in India: Strategic Considerations for CXOs January 9, 2026
- Why Enterprises Are Rethinking Their GCC Strategies in 2026 January 8, 2026
- Why Most Enterprise Expansion Strategies Fall Short of Projections, And How a GCC Enabler Can Bridge the Gap January 7, 2026
- India’s GCC Ecosystem: Why the World’s Biggest Companies Are Betting Their Future on it January 3, 2026
- Healthcare GCCs in India: Where the World’s Pharmaceutical Innovation Actually Happens January 2, 2026
- Circular Economy Models and Their Relevance to Manufacturing GCCs December 30, 2025
- GCCs in Agritech: Digitizing Global Food Security December 29, 2025
- Renewable Energy GCCs: Accelerating Global Green-Tech Development December 29, 2025
- Cyber Resilience 2030: Multi-Layer Security Architecture for GCCs December 26, 2025
- Building an Integrated Risk Management Framework for Multi-Region GCCs December 26, 2025
- The Ethics of Automation: How GCCs Maintain Human Oversight in AI Workflows December 25, 2025
- Future of HR in GCCs: Data-Led, Skills-Based, and GenAI-Driven December 25, 2025
- The Proposal to Standardize India’s GCCs for Unshakeable Global Leadership December 24, 2025
- Global Capability Centers: A Strategic Growth Model for B2B Enterprises December 24, 2025
- AI Ethics & Compliance Mandates for GCC Operations in 2025 December 23, 2025















