
Global Capability Centers (GCCs) have transformed their roles as transaction centers to become strategic engines of innovation, managing intellectual property, customer data and mission-critical workloads on clouds. The bigger GCCs grow, the bigger their attack surface: the global average cost of a data breach increased to USD 4.88 million in recent reporting, a clear sign of how much cheaper prevention is than recovery. This blog describes a prospective, practical approach to cybersecurity of GCCs, one that aligns security governance of GCCs, cloud security of GCCs, digital transformation on resilient controls and quantifiable business performance.
GCCs are at the heart of multinational activities: as the recent industry studies put it, the direct economic impact of the GCC sector is billions of dollars. It’s further rapid growth as the GCCs assume more high-value functions such as R&D, analytics, and even cloud engineering. This increasing trend renders them lucrative targets to advanced attackers in need of valuable information and destabilisation. Cybersecurity strategy for the GCC is a strategic necessity and a financial hedge; it is proactive.
In the contemporary world, threats to GCCs are most applicable to supply-chain breaches, ransomware, credential theft, and misconfigurations. Attacks targeting vendor relations and cloud integrations are increasingly used by hackers, and this trend has risen by twofold in third-party-based attacks in recent studies. Ransomware attacks and advancements in variants are on the increase, and GCCs are being put under pressure to upgrade their detection and response systems.
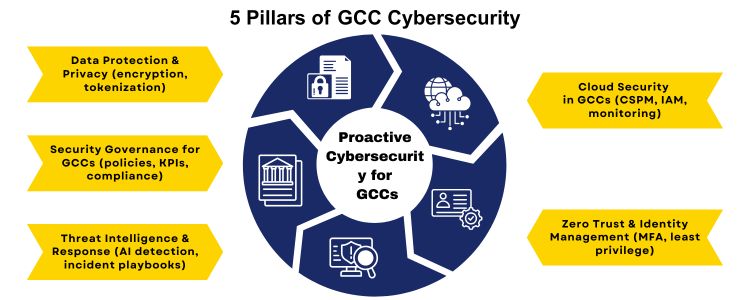
Leverage these cohesive pillars in order to develop a defensible, scaled posture between cloud and on-premises environments. 1: Security Governance of GCCs. Define a governance paradigm to align GCC security policies to parent-company risk appetite and domestically with compliance. Assign data classification, incident reporting and third-party risk ownership. Insert quantifiable KPIs (MTTD, MTTR, IAM attestations) to monitor performance. 2: Data Protection and Privacy by Design. Use encryption during motion and at rest, sensitive field tokenisation, and tough data-locality rules where policies require. Deploy a privacy impact assessment at each design cycle of a product or a platform. 3: Cloud Security within GCCs. Implement cloud-native security measures: CSPM, CWPP, cloud IAM, and automated configuration hardening. Through the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA), prioritise the protection of the most critical cloud risks based on the list of threats that are identified by practitioners. 4: Identity, Access Management and Zero Trust. Implement zero-trust concepts: least privilege, constant authentication, session tracking, and conditional access. Periodic credential hygiene and role-based access reviews help to minimise the biggest vectors of attacks. 5: Threat Intelligence, Detection and Response. Invest in SOAR and AI-assisted threat intelligence of automated containment. Keep tested incident response playbooks and tabletop exercises which contain communications, legal, and business continuity components.
An 80 per cent decrease in the critical findings during quarterly audits and a time to remediation of days to hours saw a GCC that implemented an ongoing cloud posture and zero-trust access. The investment was rewarded by preventing downtime and improving contracting conditions with enterprise customers.
As GCCs pick up the pace of digital transformation and embrace GenAI, the attack surfaces will change: model poisoning and information leakage via immediate logs, as well as AI-assisted social engineering, will become significant threats. Security should not be an afterthought but something that is embedded in the platform and is integrated with governance, secure MLOps, and validation. This change of direction towards prevention and automation is expected to increase cybersecurity revenue.
Cybersecurity is no longer a cost center to GCCs but a strategic differentiator that secures revenue, facilitates transformation to a cloud-first approach, and retains client trust. Leaders can turn risk into resilience and competitive edge by embracing security governance of GCCs, putting cloud security at the core of GCCs, and ensuring a unified cybersecurity policy of GCCs.
Contact Inductus GCC for assessment based on data flows and vendor relationships as a starting point and apply the five pillars in a prioritised sprint. The more GCC can switch to a proactive rather than a reactive mode, the more economic and reputational chips it can win: not only today but also in the era of AI.
A GCC is an offshore facility of a multinational company that undertakes niche roles such as research and development, information technology service and strategic management. It is a government program that gives the women entrepreneurs up to 1 crore in bank loans to fund greenfield projects. Personal responsibilities and unconscious bias are the factors that lead to their mid-career attrition and slow them down in their careers. They introduce new ideas, understanding, and team-oriented leadership that speeds up the advancement of such areas as AI and cybersecurity. By 2030, women are expected to take up 25-30 per cent of GCC leadership positions, which will be paramount to the growth of the Indian market. Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.
GCCs are Proactive
Economic Benefits
The Threat Landscape GCCs are Facing.
Pillars of a Proactive Cybersecurity Strategy of GCCs
Operational Table: From Risk to Action
Risk
Proactive Control
Business Outcome
Cloud misconfiguration
CSPM + automated remediations
Reduce exposed assets; faster cloud adoption
Third-party breach
Vendor risk scoring + contract SLAs
Lower downstream compromise risk
Ransomware
Immutable backups and network segmentation
Minimise downtime and financial impact
Compromised credentials
MFA + continuous session evaluation
Reduce account takeover likelihood
Case Snapshot
Future Prospectus
Conclusion
frequently asked questions (FAQs)

Aditi
Hey, like this? Why not share it with a buddy?
Related Posts
Recent Blog / Post
- Pharma GCC Setup Services in India: Strategic Considerations for CXOs January 9, 2026
- Why Enterprises Are Rethinking Their GCC Strategies in 2026 January 8, 2026
- Why Most Enterprise Expansion Strategies Fall Short of Projections, And How a GCC Enabler Can Bridge the Gap January 7, 2026
- India’s GCC Ecosystem: Why the World’s Biggest Companies Are Betting Their Future on it January 3, 2026
- Healthcare GCCs in India: Where the World’s Pharmaceutical Innovation Actually Happens January 2, 2026
- Circular Economy Models and Their Relevance to Manufacturing GCCs December 30, 2025
- GCCs in Agritech: Digitizing Global Food Security December 29, 2025
- Renewable Energy GCCs: Accelerating Global Green-Tech Development December 29, 2025
- Cyber Resilience 2030: Multi-Layer Security Architecture for GCCs December 26, 2025
- Building an Integrated Risk Management Framework for Multi-Region GCCs December 26, 2025
- The Ethics of Automation: How GCCs Maintain Human Oversight in AI Workflows December 25, 2025
- Future of HR in GCCs: Data-Led, Skills-Based, and GenAI-Driven December 25, 2025
- The Proposal to Standardize India’s GCCs for Unshakeable Global Leadership December 24, 2025
- Global Capability Centers: A Strategic Growth Model for B2B Enterprises December 24, 2025
- AI Ethics & Compliance Mandates for GCC Operations in 2025 December 23, 2025
















