
The ecosystem of Global Capability Centres (GCCs) is moving into a maturation phase in 2024-25; approximately 1,900 GCCs are based in India alone, and the GCC industry overall employs about 1.9 million professionals. The GCC industry overall makes about USD 64-65 billion in revenue, and the numbers indicate fast scales and strategic depth to the distributed delivery models. This stage requires a transition to the Multi-GCC Strategy: a conscious choice of Multi-GCCs across the regions in order to provide continuity and compliance, innovation and cost efficiency in a world getting more and more volatile. The structural response to the supply-chain shock, data-sovereignty requirements, talent fluctuations and geopolitical risk is the Multi-GCC Strategy. Multi-GCC Strategy involves letting workloads, IP, and talent spread, rather than duplicate, with three or more geographies using three or more regional GCCs (engineering, R&D, finance, and operations). It is regarding Cross-border Service Delivery that is designed to be resilient, as opposed to redundant.
Primary-Secondary Nearshore: Core product and IP in a primary GCC, failover and advanced engineering in secondary, and support/scale in nearshore. Dual-Headquartered Model: Two equal hubs have a joint strategic control to counter geopolitics. Federated Mesh: Many smaller, focused GCCs coordinated via a light global governance layer: perfect to innovate fast.
Governance: Data governance is not fragmented by the use of standardised SLAs, single toolchains, and a common source of truth. Technology: Real-time balancing is possible with cloud-native infrastructure, automated orchestration and AI-based workload routing. Cost: A TCO model that covers tax incentives, real estate and upskilling cost-swapping between quality and proximity to wage arbitrage.
The Multi-GCC Strategy will cease being a competitive edge by 2030 and become a model operating system of international business. Predict a booming GCC-orientated platform and GCC-as-a-Service provider industry, where companies can spin up regional capability in a cost-effective way. Even the GCC market alone is expected to grow significantly over the decade, making the first to adopt the multi-hubs the most resilient and quickest-innovating companies.
Multi-GCC is not an IT project; it is a business stance strategy that transforms regional delivery into resilience, compliance, innovation and cost leadership. Resilience will become a competitive advantage where organizations come up with regional-intended designs of delivery, a combination of governance, technology and economics.
A GDC refers to a single-minded offshore deployment, which provides proficient business, technology and operational services to corporate bodies on a global basis. BFSI, IT services, healthcare, telecom, retail, manufacturing, and other upcoming technologies, including AI and blockchain. They do not only target cost savings but now aim at innovation, automation, R&D, digital transformation, and high-value consulting. They design and create cloud, artificial intelligence, analytics, cloud security, and process automation. A large supply of STEM graduates, multilingual workers and niche skills in AI, ML, cloud, and analytics. Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.
Why Regional Delivery Models Have Become Business Critical:
Business Advantages & Economic Impact
Strategic Power
How it Works
Business & Economic Advantage
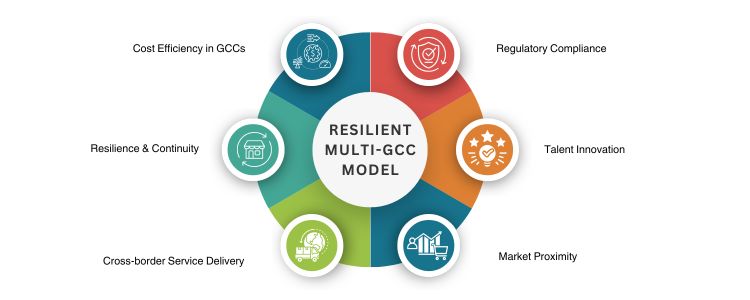
Resilience & Continuity
Live failover and workload balancing across GCCs
Minimises downtime; protects revenue and reputation
Regulatory Localisation
Data residency and local compliance by design
Reduces fines and speeds market entry
Cost Efficiency in GCCs
Mix of labour cost arbitrage and productivity gains
Lower TCO; predictable operating margins
Talent & Innovation Density
Leverage regional specialisations (AI, cloud, R&D).
Faster product cycles; higher IP yield
Market Proximity
Local teams for product localisation and CX
Higher conversion, faster feedback loops
Economic Multipliers
GCC investments spur local job creation & services.
GDP contribution, urban ecosystem growth.
Practical Multi-GCC Architecture
Governance, Technology and Cost Considerations
Challenges & Strategy
Future Prospect
Conclusion
frequently asked questions (FAQs)

Aditi
Hey, like this? Why not share it with a buddy?
Related Posts
Recent Blog / Post
- Pharma GCC Setup Services in India: Strategic Considerations for CXOs January 9, 2026
- Why Enterprises Are Rethinking Their GCC Strategies in 2026 January 8, 2026
- Why Most Enterprise Expansion Strategies Fall Short of Projections, And How a GCC Enabler Can Bridge the Gap January 7, 2026
- India’s GCC Ecosystem: Why the World’s Biggest Companies Are Betting Their Future on it January 3, 2026
- Healthcare GCCs in India: Where the World’s Pharmaceutical Innovation Actually Happens January 2, 2026
- Circular Economy Models and Their Relevance to Manufacturing GCCs December 30, 2025
- GCCs in Agritech: Digitizing Global Food Security December 29, 2025
- Renewable Energy GCCs: Accelerating Global Green-Tech Development December 29, 2025
- Cyber Resilience 2030: Multi-Layer Security Architecture for GCCs December 26, 2025
- Building an Integrated Risk Management Framework for Multi-Region GCCs December 26, 2025
- The Ethics of Automation: How GCCs Maintain Human Oversight in AI Workflows December 25, 2025
- Future of HR in GCCs: Data-Led, Skills-Based, and GenAI-Driven December 25, 2025
- The Proposal to Standardize India’s GCCs for Unshakeable Global Leadership December 24, 2025
- Global Capability Centers: A Strategic Growth Model for B2B Enterprises December 24, 2025
- AI Ethics & Compliance Mandates for GCC Operations in 2025 December 23, 2025
















