
When a global technology company broke the news last year that most of its latest algorithms and patents were being written at its centers in Bengaluru and Pune, the industry took notice that Global capability centres are no longer just offshore delivery centers or cost hubs but are engines of corporate R&D and proactive generators of intellectual property. This change is getting significant to companies aiming to become AI, semiconductor, fintech, and life sciences leaders, and to national innovation systems acquiring high-paying jobs and exportable research and development. Recent statistics indicate that India has the highest number of GCCs in the world, with figures of about 1,900+ centers estimated to bring over USD 60-65 billion of value every year and close to two million professionals, and that trend is only increasing. Businesses are in incessant demand to make innovations quicker and defend what they create. Increasingly, a contemporary Global R&D strategy has offshore R&D centers and GCCs at the center of product roadmaps rather than in the periphery. GCCs merge domain talent, product engineering, data science, and regulatory know-how in teams that are coherent enough to deliver the prototypes, pilots, and patentable results across the time zones on a continuous basis. The change in capability can be observed in that year after year GCC revenues and headcount continue to increase and in that the Indian states are making policy changes to encourage more centers as part of strategic investment.
GCCs have access to huge pools of engineers, data scientists and domain experts. Being close to universities, incubators and startups forms an innovation cycle: academic knowledge input transforms into product experiments, which become deployable IP. The current trend is that multinational companies have established sophisticated ML, embedded systems and drug-discovery divisions within the Indian GCCs to exploit the depth of talent as well as cost advantage. In contrast to the older and isolated offshore delivery centres, a contemporary GCC implements the use of agile pods that take responsibility for a complete product design, build, test and iterate. This full-fleet ownership reduces the R&D cycle and the chance that prototypes will be proprietary assets. Quick iteration results in a shorter time to patent and increased market commercialisation. GCCs are becoming more co-created with local startups and centres of excellence, with IP roadmaps and joint offers. This co-innovation reduces technical risk and creates hybrid IP (joint patents, licensed modules and platform components) that has different commercial value. Businesses are also patenting at their offshore R&D sites, and government structures within GCCs now incorporate IP strategy, patent scouting and defensible architecture design. This trend is replicated in the increasing position of India in patent filing: since 2005, national filings and grants have been steadily increasing, highlighting the role of local R&D in the IP portfolio around the world.
The rows reflect each and every line of work as a direct lineage between work within an offshore R&D centre and quantifiable IP and commercial value
The trend is enhanced by policy and industry signals. In a number of Indian states and governments, GCC incentives are being rolled out to get investment and create employment; corporations are openly stating their intentions to move larger proportions of global R&D to their Indian centres. Indicatively, the recent state policies are focused on the growth of GCCs in tier-2 and tier-3 cities to facilitate regional growth as well as diversified talent pipelines. The output of offshore intellectual property will also increase as businesses grow more comfortable taking full ownership of offshore product development centres.
Global capability centres have been developed out of offshore delivery centres, which have turned into strategic sources of innovation. When enterprises consider GCCs as true partners in their Global R&D strategy, i.e., explicit IP management, investment in local ecosystems, and ownership of products, the rewards are high: accelerated innovation, defensible IP, and sustainable cost benefits. The future belongs to those organisations that not only design their GCCs but also create to make offshore capability their global competitive advantage.
Contact Inductus Gcc while reconsidering your Global R&D strategy or considering an Offshore R&D Location. Begin with realigning GCC structure to IP goals: establish ownership, invest in talent pools, and develop co-innovation structures. The reward will be the number of patents, products and market leadership.
A GCC is an offshore facility of a multinational company that undertakes niche roles such as research and development, information technology service and strategic management. It is a government program that gives the women entrepreneurs up to 1 crore in bank loans to fund greenfield projects. Personal responsibilities and unconscious bias are the factors that lead to their mid-career attrition and slow them down in their careers. They introduce new ideas, understanding, and team-oriented leadership that speeds up the advancement of such areas as AI and cybersecurity. By 2030, women are expected to take up 25-30 per cent of GCC leadership positions, which will be paramount to the growth of the Indian market. Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.
Four Pillars For R&D and IP Development
1) Deep-Tech Talent and Knowledge Agglomeration
2) Agile, Product-Based R&D Models
3) Co-Innovation With Startups and Academia
4) Strategic IP Ownership And Governance
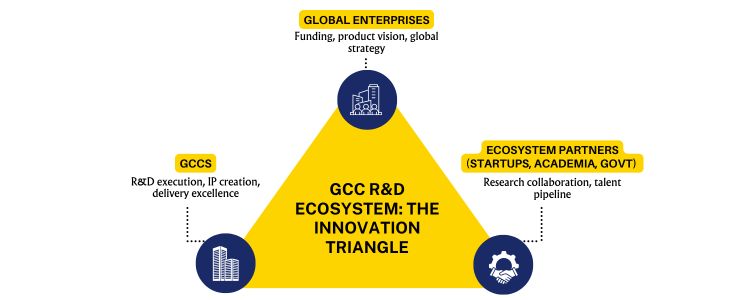
Why Companies Invest in GCC-Based R&D
GCC-Driven R&D Impact Areas
Focus Area
GCC Role
Outcome (R&D / IP)
AI & Automation
Build proprietary ML models, MLOps platforms
Model patents, algorithmic IP
Semiconductors & Hardware
Chip design, verification labs
Design patents, test IP
Healthcare Tech
Clinical analytics, digital therapeutics
Data-driven medical IP
FinTech & RegTech
Payments architecture, compliance engines
Process & security patents
Sustainability
Energy modelling, carbon analytics
Green-tech IP and standards
Present And The Future
Conclusion

Aditi
Hey, like this? Why not share it with a buddy?
Related Posts
Recent Blog / Post
- The Role of GCCs in Accelerating Corporate R&D and IP Creation November 4, 2025
- Navigating Geopolitical Risks: A Guide for GCC Leaders November 4, 2025
- Why Mid-Sized Companies are Embracing the GCC Model October 16, 2025
- What Is A Global Capability Center (GCC), and Why Is It Essential For Modern Business? October 16, 2025
- Gurugram’s Tech Ascent: Decoding the New Haryana GCC Policy October 15, 2025
- Scaling Your Tech Team: A Beginner’s Look at the Offshore Development Center October 15, 2025
- Agile Methodologies for GCCs: A Blueprint for Success October 6, 2025
- The Legal and Compliance Checklist for a New GCC Setup October 4, 2025
- The Rise of Niche GCCs: A Focus on Specialised Capabilities October 4, 2025
- The Impact of Regulatory Changes on GCC Operations October 4, 2025
- Cybersecurity for GCCs: A Proactive Approach to Data Protection September 30, 2025
- Beyond Cost: Measuring the True ROI of Your GCC Investment September 29, 2025
- The Future of GCCs in the Retail Sector: A Strategic Playbook September 29, 2025
- David vs Goliath: Mid-Sized GCCs Quietly Outperform the Big Brands September 29, 2025
- Infineon’s Big Bet on India: Inside Its First GCC in GIFT City September 29, 2025
















