Global Capability Centers (GCCs) cease to be cost-cutting expansion nodes in 2025: the springboards of enterprise innovation. The latest surveys indicate an extremely steep increase in the number of organizations shifting beyond isolated pilots to production-level applications, and GCCs become the epicenter of this transition. India by itself has nearly two thousand GCCs, and most of them are re-architecting delivery models to incorporate Gen AI into every aspect of their operations, such as compliance and finance, product engineering, and customer experience. Such actions bring quantifiable economic benefits: increased productivity, reduced time to market and material cost efficiency, as well as generating new AI-native jobs. In order to prove technical viability and regulatory fit, the pilot-to-scale experience in Global In-House Centers (GICs) frequently began with targeted experiments, chatbots, summarization assistants, and model-based forecasting. Pilots were realistic: data management issues, untied ROI, and underdeveloped toolchains required small and contained initiatives. However, in 2025 the situation has changed. The focus of the enterprise leaders and GCC heads currently is on industrialization: process repetition, solid management of models, and operationalized MLOps to convert prototypes into services that can withstand change and be audited. The outcome is that impact has changed; pilot outcomes will provide quantifiable business metrics, rather than demonstrating a proof of concept.
Predictability, responsibility, and value extraction are more than scale in industrializing Gen AI across GCCs. When it is being industrialized in a Global Capability Center, the following can be observed: These consequences are important because businesses are no longer evaluating Gen AI as an experiment to carry out; they are considering it as a productive factor and a strategic asset.
This small structure assists GCC leaders to turn single-win achievements into enterprise-level capabilities which are resilient, auditable and repeatable. GCC is Restructuring to Industrialise Gen AI. It is possible to see three practical changes in high-performing GCCs: From Labs to Studios—Pilot labs are becoming AI Studios and CoEs that deliver life cycle, rather than experimentation. Strategic Partnerships GCCs – It collaborates with hyperscalers, niche GenAI startups and academic laboratories to more quickly construct capacity and economically reach specialised models. Governance Boards – Institutionalises the control of risk and business alignment through multi-stakeholder AI boards (CDO, CIO, legal, business heads) These changes are measurable. Top GCCs claim more rapid model turnaround, greater business user adoption, and easier ROI tracking.
Machines are necessary for industrialisation, but humans are the ones who must achieve it. The automation is able to eradicate old jobs and at the same time generate new jobs with higher value like AI coordinators, model auditors, and domain-AI specialists. The GCCs that make investments in organized reskilling and role redefinition appropriate net economic value: they reduce repetitive labor, boost employee productivity, and reallocate human capital to jobs where domain knowledge and judgment are essential. Similar concerns are held by national and regional policy bodies, which focus on reskilling to achieve both efficiency gains and jobs.
Companies that are developing industrialised GenAI in their GCCs cite a number of distinct economic benefits: The macro-level analyses predict that AI will significantly boost GDP growth and national productivity over the next ten years, making GCC investments in industrialization both strategically and financially imperative. What’s Next? By 2030, anticipate that GCCs will be turned into AI-native, not just AI-enabled, strategic hubs. Interfaces will be constantly learning, self-optimising and democratising innovation with low-code/no-code interfaces and built-in copilots. Regardless, the responsible deployment of AI will continue to be a determinant variable; when paired with sound governance, enterprises that embrace aggressive scaling and still manage to create value will avoid systemic risk at the same time.
Global Capability Centers and Gen AI will not be evaluated by the number of pilots launched in the future; they will be evaluated by the number of capabilities industrialised. The decade of global delivery that lies ahead will be characterised by GCCs which decisively break their experimentation with implementations that are enterprise substantial, to the extent that they provide economic value, operational durability and a novel type of human-computer cooperation.
A GCC is an offshore facility of a multinational company that undertakes niche roles such as research and development, information technology service and strategic management. It is a government program that gives the women entrepreneurs up to 1 crore in bank loans to fund greenfield projects. Personal responsibilities and unconscious bias are the factors that lead to their mid-career attrition and slow them down in their careers. They introduce new ideas, understanding, and team-oriented leadership that speeds up the advancement of such areas as AI and cybersecurity. By 2030, women are expected to take up 25-30 per cent of GCC leadership positions, which will be paramount to the growth of the Indian market. Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.
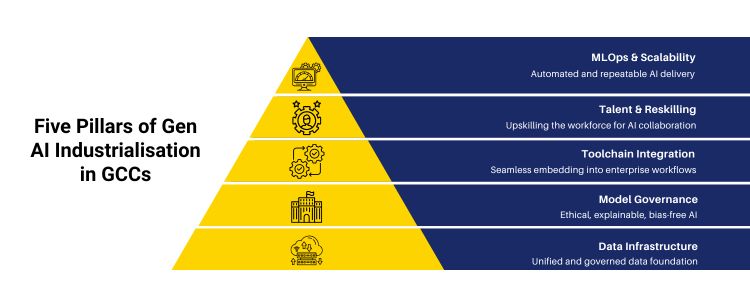
Significance of Industrialisation
GenAI AI Industrialisation in GCCs.
Pillar
What it delivers
GCC action example
Data Infrastructure
One common, governed, data-based foundation of model training and model inference.
Centralised AI data lake with regional access control.
Model Governance
Safety, bias tests, explainability and compliance
Model responsible audit trails and artificial intelligence structures.
Toolchain Integration
Efficient integration of AI with ERP, CRM and workflows.
AI copilots were incorporated in service- desk systems and finance systems.
MLOps & Scalability
Auto CI/CD, monitoring, and drift detection.
The Central AI operation team has automated deployment pipelines.
Talent & Culture
Reskilling, new position design, incentives to adopt.
Quick education in engineering and AI literacy
Reskilling and Economic Opportunity
Economic Benefits
Conclusion
frequently asked questions (FAQs)

Aditi
Hey, like this? Why not share it with a buddy?
Related Posts
Recent Blog / Post
- Pharma GCC Setup Services in India: Strategic Considerations for CXOs January 9, 2026
- Why Enterprises Are Rethinking Their GCC Strategies in 2026 January 8, 2026
- Why Most Enterprise Expansion Strategies Fall Short of Projections, And How a GCC Enabler Can Bridge the Gap January 7, 2026
- India’s GCC Ecosystem: Why the World’s Biggest Companies Are Betting Their Future on it January 3, 2026
- Healthcare GCCs in India: Where the World’s Pharmaceutical Innovation Actually Happens January 2, 2026
- Circular Economy Models and Their Relevance to Manufacturing GCCs December 30, 2025
- GCCs in Agritech: Digitizing Global Food Security December 29, 2025
- Renewable Energy GCCs: Accelerating Global Green-Tech Development December 29, 2025
- Cyber Resilience 2030: Multi-Layer Security Architecture for GCCs December 26, 2025
- Building an Integrated Risk Management Framework for Multi-Region GCCs December 26, 2025
- The Ethics of Automation: How GCCs Maintain Human Oversight in AI Workflows December 25, 2025
- Future of HR in GCCs: Data-Led, Skills-Based, and GenAI-Driven December 25, 2025
- The Proposal to Standardize India’s GCCs for Unshakeable Global Leadership December 24, 2025
- Global Capability Centers: A Strategic Growth Model for B2B Enterprises December 24, 2025
- AI Ethics & Compliance Mandates for GCC Operations in 2025 December 23, 2025