
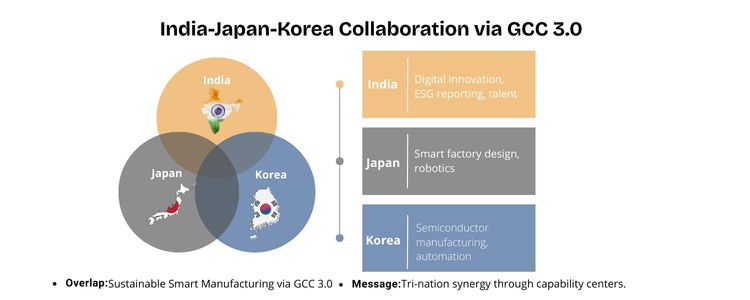
The flourishing digital transformation skills, especially in offering ultimate technological solutions, of India are playing a significant role in world industrial development. The market of smart manufacturing currently experiences hyperbolic growth, and it is expected to reach USD 620.17 billion by 2028 with a 12.2% CAGR between 2021 and 2028 (Fortune Business Insights). This boom holds great potential in allowing Indian technology vendors such as GCC to provide customised services on an international level, resulting in economic growth in India due to the output of exports and technological advancements. Revolving around the super powerhouse economies of Japan and Korea, this blog proposes a strategic playbook in embracing Sustainable Smart Manufacturing enabled through our end-to-end GCC 3.0 framework.
Japan and Korea, which are famous for having the power to manufacture, encounter some transforming challenges. A greying workforce, rising energy prices, increases in strict environmental controls, and the unending drive to innovate all require a paradigm change. As the 2023 World Manufacturing Production Report by UNIDO shows, pressure in the two nations to up efficiency and sustainability is growing in an effort to stay competitive. Smart technologies provide a means to rise to the challenges, making use of resources more effective with a lower negative impact on the environment.
GCC 3.0 is a framework to support the transition to Sustainable Smart Manufacturing. It incorporates advanced analytics, the Internet of Things, and artificially intelligent-based insights so that manufacturing organisations have previously unmatched access and control over their operations. We have an environmentally conscious strategy that focuses on increasing the efficiency of the operations without compromising the environment. GCC 3.0 provides real-time analyses on data to optimise the use of energy, forecasts the capabilities to achieve minimal waste, imparts quality control, and promotes the circular economy principles of the production process. Due to the modular nature of its platform, the platform integrates easily with current infrastructure.
Our Japanese and Korean manufacturers playbook has a simple phased playbook: Foundation & Planning: This step in the process requires a thorough analysis of current manufacturing techniques and processes that could benefit the most from improvement and what pilots would best determine the effectiveness of GCC 3.0. It is the most crucial thing to synchronise its strategies with business objectives and sustainability goals. Implementation and Integration: Here, the focus is about the technical installation of the GCC 3.0 platform and how to integrate the data amongst various systems quite well. The new technologies and working patterns would be coherently used in the labour pool through extensive training systems. Scaling & Optimisation: Since pilot programmes have been used successfully, an effort is subsequently made to expand the GCC 3.0 framework to the rest of the manufacturing enterprise. This ability to optimise continuously and eventually guarantee the improvements of performance and the achievement of key performance indicators (KPIs) is only enabled by the process of continuous monitoring and data analytics.
To enable the successful embrace of the Sustainable Smart Manufacturing, a collaborative ecosystem is a requirement. GCC has been very active in the area of relationship building with the technology providers as well as government agencies and industry associations both in Japan and Korea. We also pay much attention to utilise the available policy models as well as search available stimulus packages facilitating green manufacturing and digital transformation programmes. An effective workforce upskilling plan is also part of the equation to make the human capital capable of handling and harnessing the potential of GCC 3.0.
Sustainable Smart Manufacturing with GCC 3.0 is associated with economic benefits. Through the optimal usage of resources, manufacturers can make their cost savings significant both in terms of energy and raw material. A boost in operational efficiency results in a boost in productivity and downtime. Furthermore, the adoption of sustainable activities can boost the reputation of the brand and respond to the increased need for goods that are environmentally friendly. There are quantifiable criteria of the initiative that illustrate a definite rate of return on investments (ROI), which contributes to long-term business resilience (carbon savings, efficiency gains). GCC in india seeks to enable Japanese and Korean manufacturers to continue exploring a brighter world towards a sustainable, efficient and technologically advanced future. With our capability and the extensive GCC 3.0 framework, there exists an evident trend of 21st-century excellence in the manufacturing cycle. To sum up, switching to Sustainable Smart Manufacturing with GCC 3.0 as its driving force is an opportunity that Japan and Korea could grasp to improve their competitiveness on the international market.
Indian firms such as Inductus GCC, this has offered them the opportunity to utilise our technological expertise and export our technology to these major economies to shape their industrial growth, adding to each other’s economies. For more in-depth information, we recommend reading A Business Case For South Korean MNCS and A GCC Business Case for Japanese MNCs issued by Inductus GCC.
Data analytics centralisation, greater streamlining of production lines, and the use of ESG metrics as part of KPIs in operations. Sophisticated manufacturing ecosystems, green growth and net-zero government incentives, and the high-tech infrastructure. Three things: the high-tech ecosystems of manufacturing, the green growth and net-zero government incentives, and the high-tech infrastructure. The experienced engineers, ESG consultants and AI specialists can ensure the fast implementation of clean tech and circular manufacturing models. Better energy performance, regulatory commands, quicker product innovation and competitiveness worldwide using sustainable Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.
The Japan and Korean Transformation Imperative
GCC 3.0: Towards Sustainable and Smart Factories
An Implementation Strategic Roadmap
Phase
Key Activities
Key Outcomes
Foundation & Planning
Assessment, Strategy Development, Pilot Project Selection
Clear Objectives, Defined Scope, Identified KPIs
Implementation & Integration
Platform Deployment, Data Integration, Workforce Training
Operational GCC 3.0 System, Integrated Data Streams, Skilled Workforce
Scaling & Optimisation
Enterprise-wide Rollout, Continuous Monitoring, Advanced Analytics Application
Optimised Processes, Data-Driven Decisions, Sustained Performance Improvement
Creation of a Collaborative Ecosystem
Showing Business Impact
frequently asked questions (FAQs)

Aditi
Hey, like this? Why not share it with a buddy?
Related Posts
Recent Blog / Post
- Agile Methodologies for GCCs: A Blueprint for Success October 6, 2025
- The Legal and Compliance Checklist for a New GCC Setup October 4, 2025
- The Rise of Niche GCCs: A Focus on Specialised Capabilities October 4, 2025
- The Impact of Regulatory Changes on GCC Operations October 4, 2025
- Cybersecurity for GCCs: A Proactive Approach to Data Protection September 30, 2025
- Beyond Cost: Measuring the True ROI of Your GCC Investment September 29, 2025
- The Future of GCCs in the Retail Sector: A Strategic Playbook September 29, 2025
- David vs Goliath: Mid-Sized GCCs Quietly Outperform the Big Brands September 29, 2025
- Infineon’s Big Bet on India: Inside Its First GCC in GIFT City September 29, 2025
- From Campuses to Capability Centres: How Indian Universities Power the Global GCC Ecosystem September 29, 2025
- Retail Meets Digital: Costco’s GCC in Hyderabad Marks a Global Shift September 29, 2025
- The Silent Crisis: Why Many GCCs Plateau After 3 Years and How to Avoid It September 24, 2025
- Germany’s New Skilled Immigration Act and Its Ripple Effect on the GCC Talent Model September 24, 2025
- From Tokyo to Hyderabad: The Future of GCCs for Japanese Conglomerates September 23, 2025
- GCCs as AI Acceleration Hubs: Collaborating with US and Nordic Tech Majors September 19, 2025
















