
Creating a Global Capability Centre (GCC) right away in an ecosystem that can expand faster than most teams. India has over 1,900 GCCs with approximately 1.9 million professionals, producing over USD 64 billion of direct output as GCCs become centres of capability rather than cost. These data do not just indicate scale but also a trend & projections that India will have significantly increased GCC revenue and number of heads by the year 2030. The establishment of a GCC is a strategic move. It is on the business formation but needs a legal and compliance base which transforms regulatory complexities into competitive benefits. The following checklist is both future-focused and practical, as well as in order, allowing business value to be created faster rather than slower as a result of the legal choices made.
GCCs will move more up the value chain in the next decade in product engineering, AI R&D, regulated financial services and domain IP. This makes data protection, workforce laws, tax regulations in the GCC, and contractual transparency vital. Compliant GCC mitigates risk, makes cash flows predictable and unlocks government incentives to enhance profit margins and speed to market. The economic benefits of location planning and incentive capture are reflected by recent state and central policies which have attempted to increase GCC penetration into Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities.
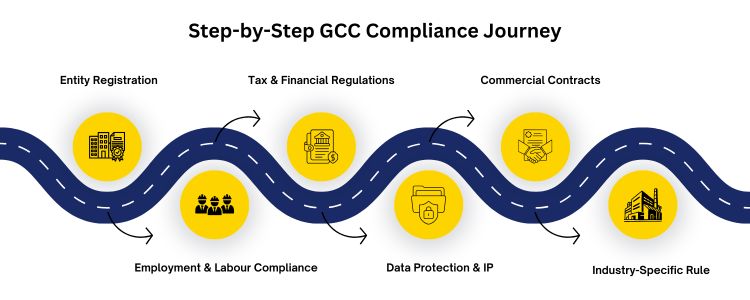
1) Entity/Corporate Set-Up. 2) Employment, Labour and Mobility 3) Financial and Tax Compliance 4) Data Protection, Security and IP 5) Commercial and Real Estate Contracts 6) Industry-Related Rules and Certifications.
Risk Management for GCC businesses is an ongoing process, like introducing quarterly compliance reviews and ensuring that legal reviews are included in the hiring, procurement and product release processes. Errors such as expecting home country policy to work, procrastinating transfer pricing documentation, or poor IP assignment language may all result in fines, litigation or loss of strategic assets.
The process of starting a business in GCC form must have its legal accuracy and a compliance rhythm that will increase with ambition. The checklist mentioned above translates regulatory requirements into a predictable launch schedule: select the appropriate entity, operationalise compliance with employment and taxation, fortify data and IP controls, and maintain a watch on industry-specific regulations.
When compliance is strategic, GCCs shift more quickly into higher-value work, making the centre more of an engine of innovation and development rather than a transaction hub.
A GCC is an offshore facility of a multinational company that undertakes niche roles such as research and development, information technology service and strategic management. It is a government program that gives the women entrepreneurs up to 1 crore in bank loans to fund greenfield projects. Personal responsibilities and unconscious bias are the factors that lead to their mid-career attrition and slow them down in their careers. They introduce new ideas, understanding, and team-oriented leadership that speeds up the advancement of such areas as AI and cybersecurity. By 2030, women are expected to take up 25-30 per cent of GCC leadership positions, which will be paramount to the growth of the Indian market. Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.
Introduction
Core Legal & Compliance Checklist
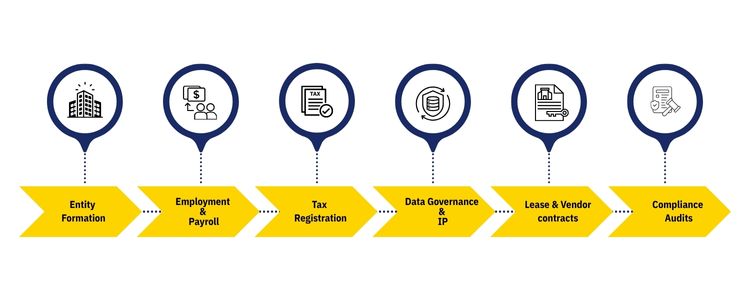
Legal & Compliance
Area
Key Actions
Target timeline
Entity & Registration
ROC, PAN, GST — choose structure
0–30 days
Employment & Payroll
Contracts, PF/ESI, payroll set-up
15–60 days
Tax & Transfer Pricing
GST, TDS, TP policy
30–90 days
Data & Security
DPDP alignment, incident plan
30–120 days
Commercial Contracts
Lease, vendor & customer templates
15–90 days
Industry Certs
RBI/SEBI, healthcare, export controls
Ongoing
Risk Management and Pitfalls
Conclusion
frequently asked questions (FAQs)

Aditi
Hey, like this? Why not share it with a buddy?
Related Posts
Recent Blog / Post
- The Legal and Compliance Checklist for a New GCC Setup October 4, 2025
- The Rise of Niche GCCs: A Focus on Specialised Capabilities October 4, 2025
- The Impact of Regulatory Changes on GCC Operations October 4, 2025
- Cybersecurity for GCCs: A Proactive Approach to Data Protection September 30, 2025
- Beyond Cost: Measuring the True ROI of Your GCC Investment September 29, 2025
- The Future of GCCs in the Retail Sector: A Strategic Playbook September 29, 2025
- David vs Goliath: Mid-Sized GCCs Quietly Outperform the Big Brands September 29, 2025
- Infineon’s Big Bet on India: Inside Its First GCC in GIFT City September 29, 2025
- From Campuses to Capability Centres: How Indian Universities Power the Global GCC Ecosystem September 29, 2025
- Retail Meets Digital: Costco’s GCC in Hyderabad Marks a Global Shift September 29, 2025
- The Silent Crisis: Why Many GCCs Plateau After 3 Years and How to Avoid It September 24, 2025
- Germany’s New Skilled Immigration Act and Its Ripple Effect on the GCC Talent Model September 24, 2025
- From Tokyo to Hyderabad: The Future of GCCs for Japanese Conglomerates September 23, 2025
- GCCs as AI Acceleration Hubs: Collaborating with US and Nordic Tech Majors September 19, 2025
- Breaking the Tech Ceiling: How Women Leaders Are Reshaping India’s GCC Landscape September 19, 2025
















