
The Global Capability Centres (GCCs) change the method of management of global operations, supply chains, and innovation ecosystems of multinational companies. Once seen as back-office units, GCCs have developed as strategic control centers in India that affect the production, distribution, and innovation of businesses in global markets. In the last two decades, GCC has quietly redefined global trade by centralising commercial operations, controlling supply chains, and furthering digital changes from cost-skilled centres like India. Today, they are changing economic power corridors by broadcasting high-value works in the metros and emerging Tier-II cities. As the global value chains are becoming more complex and sensitive to disruption, GCC in India will continue to shape outsourcing and global business by acting as intelligent, flexible control centers that strengthen trade continuity and development worldwide. India already operates more than 1,900 GCCs, and by 2030, an 8–10% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is estimated. India is at the centre of this change.
Modern GCCs act as strategic business units, which manage important areas such as supply chain flexibility, purchase adaptation, real-time analysis, research and development, and AI-operated customer aids. These companies are able to work fast, reduce costs, and promote innovations globally; all these tasks are managed from centers in India. India’s advantage is clear:
In today’s connected economy, GCCs play an important role in supply chain transformation as control towers of global supply chains. In India, how they manage and optimise each important phase of the supply chain is mentioned here: By using large data and machine learning, GCCs estimate market demands, adapt stock levels, and help companies to fulfil customers’ expectations efficiently. GCC, using AI-powered analysis, continuously analyses the performance, costs, and risks of suppliers, ensuring that companies work with the most reliable suppliers globally. GCC in India production processes are monitored in real time to ensure uninterrupted flow of raw materials and components and to monitor global logistics. All data collected by GCC is converted into actionable insights to reduce costs, reduce distribution time, and improve the overall supply chain flexibility.
India’s GCC is the global center of specific talent. The availability of talent is highlighting India as a global GCC leader.
By consolidating global operations in India, business promotes the following: Diversification of geopolitical risk while centralizing operational information.
GCC is now a global launchpad due to:
India’s GCC growth by 2030 will act as an autonomous commercial ecosystem, which will promote the following:
The global capability centre (GCC) is no longer only operating engines. They are command centers with strength in global trade and innovation. By streamlining global value chains, speeding up supply chain changes, and promoting innovation, GCCs are giving a new look to the way of operating multinational companies in India.
For the future, for businesses seeking flexible development models, India’s GCC ecosystem provides unmatched talent, cost profit, and measurement. The future of outsourcing lies in the creation of strategic GCCs in India, which will convert operations into global economy control centres. To set up a world-class global capability center in India, partner with your reliable Inductus GCC. From strategy to implementation, we help you to create flexible, innovative, and cost-influential GCCs that strengthen your global operation. Make India your next strategic command hub.
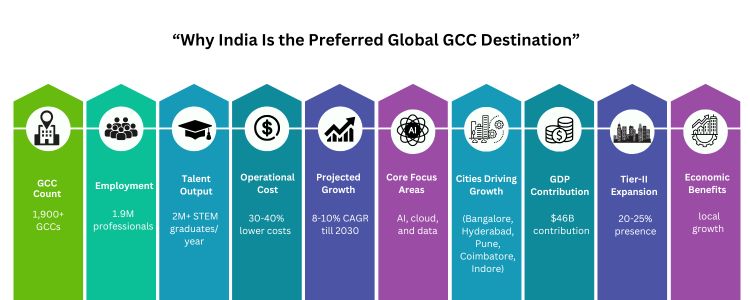
India has a huge digital talent pool, 30–40% cost savings, strong infrastructure, and a subsidiary policy environment that makes it a favourite destination for GCC. India’s GCCs serve as strategic control centres, which manage supply chains, innovation, customer services, and operations for global businesses. GCCs contribute more than $64 billion to India’s GDP and produce employment for about 19 million professionals, which promotes infrastructure and regional development. Yes. By 2030, 30–35% of new GCC is expected to be established in Tier-2 cities such as Indore, Coimbatore, and Visakhapatnam, which will spread economic benefits. India’s GCC region is expected to grow at an 8–10% compound annual growth rate (CAGR), which is estimated to be more than 2,000 and contributing to GDP (GDP) to be more than $70 billion. Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.
From Operational Units to Strategic Command Hubs
Supply Series Command Layer
Talent as Capital
Economic Power Corridor
Innovation Distribution Centre
Future Approach
Conclusion
frequently asked questions (FAQs)

Aditi
Hey, like this? Why not share it with a buddy?
Related Posts
Recent Blog / Post
- Agile Methodologies for GCCs: A Blueprint for Success October 6, 2025
- The Legal and Compliance Checklist for a New GCC Setup October 4, 2025
- The Rise of Niche GCCs: A Focus on Specialised Capabilities October 4, 2025
- The Impact of Regulatory Changes on GCC Operations October 4, 2025
- Cybersecurity for GCCs: A Proactive Approach to Data Protection September 30, 2025
- Beyond Cost: Measuring the True ROI of Your GCC Investment September 29, 2025
- The Future of GCCs in the Retail Sector: A Strategic Playbook September 29, 2025
- David vs Goliath: Mid-Sized GCCs Quietly Outperform the Big Brands September 29, 2025
- Infineon’s Big Bet on India: Inside Its First GCC in GIFT City September 29, 2025
- From Campuses to Capability Centres: How Indian Universities Power the Global GCC Ecosystem September 29, 2025
- Retail Meets Digital: Costco’s GCC in Hyderabad Marks a Global Shift September 29, 2025
- The Silent Crisis: Why Many GCCs Plateau After 3 Years and How to Avoid It September 24, 2025
- Germany’s New Skilled Immigration Act and Its Ripple Effect on the GCC Talent Model September 24, 2025
- From Tokyo to Hyderabad: The Future of GCCs for Japanese Conglomerates September 23, 2025
- GCCs as AI Acceleration Hubs: Collaborating with US and Nordic Tech Majors September 19, 2025
















