
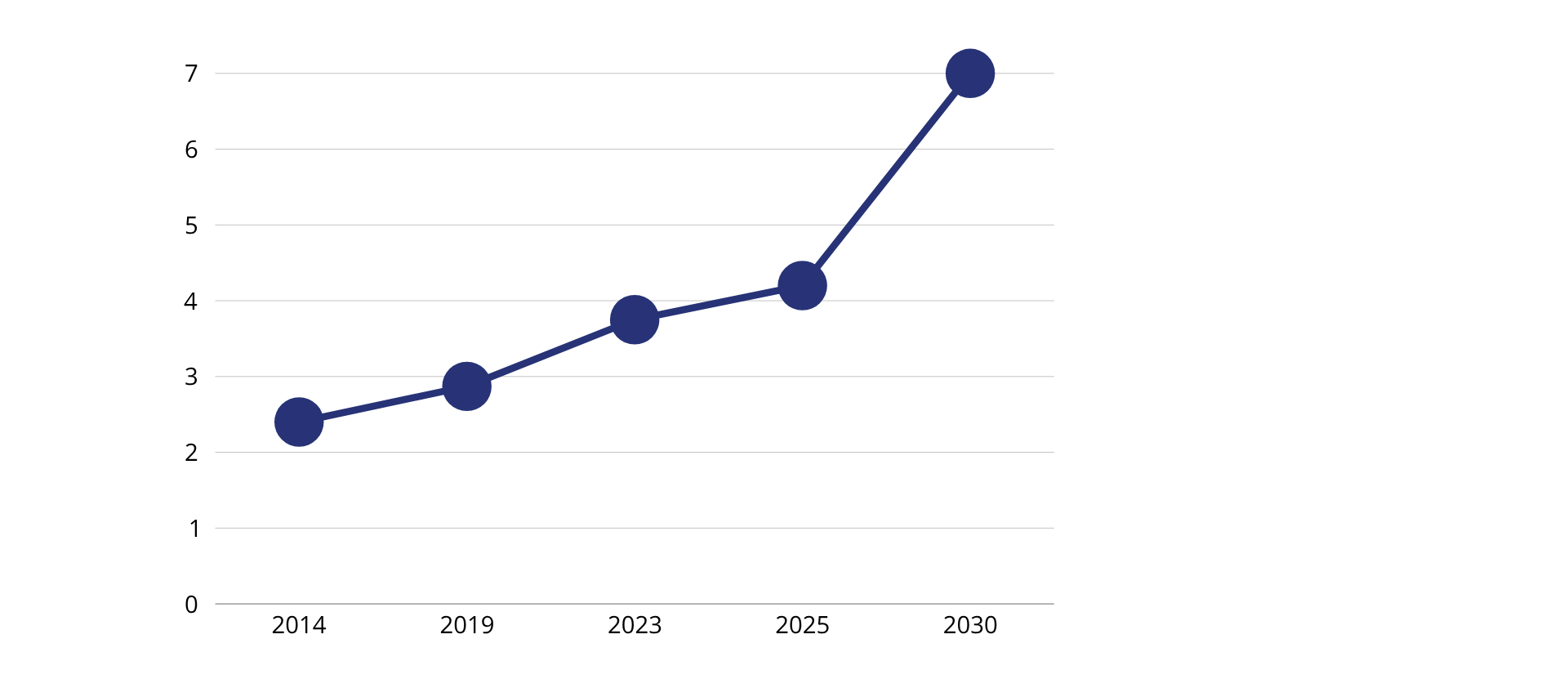
India’s status as the world’s favourite destination for global capability centers (GCC) is not a chance; this is a sustainable and strategic policy push. In the last decade, India has transformed into a global destination for digital strategy and innovation. Enterprises have changed from low-cost IT outsourcing center to offshore development centers. The development of global capacity centers (GCC) in India has been at the center of this change. This is the direct result of visionary policy steps by both the Government of India and the active state administration. In 2014, India’s GDP was $2.04 trillion. At that time, India’s digital and global distribution capabilities were underdeveloped, which were interrupted by infrastructure deficiencies and regulatory obstacles. Growing forward in 2023, India’s GDP increased to $3.73 trillion due to digital India, ease of doing business reforms, and PLI schemes such as policy implementation. India is expected to reach the GDP of $7 trillion by 2030, and by 2026, the GCC is expected to contribute more than 110 billion dollars. India has now become a home to 45% of all global GCCs, which not only provides cost benefits but also leadership in AI, Analytics, Research and Development, Stability Platforms and cybersecurity. Due to working closely with the policies of the centre and the state, India is established as a strategic lever for GCC ecosystem enterprise development.
The federal government of India has laid the foundation of a rich India GCC policy that enables innovation, digital scale, and cost-effective distribution directly. Here it is described: These policy steps reduced the time taken in installation, freed global operations, and promoted confidence in India’s digital rule.
Central policies prepared the base, while the state governments provided differential values: infrastructure, skill development, tax exemption, and startup collaboration. These localised incentives reduce operating costs, improve access to talent, and enable the firms to diversify the metros.
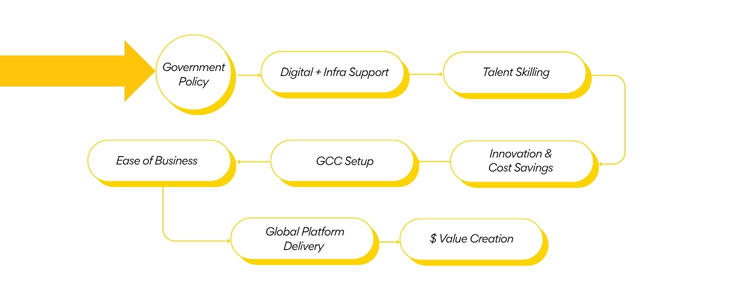
The success of GCC in India lies in a self-righteous policy. It acts as follows: This cycle flourishes and establishes India not only as a cost-out destination but also as a global innovation partner. This development is reflected in the development of platform-based GCCs in areas such as AI, Analytics, Cloud Transformation and cybersecurity across India.
Each policy lever activates a basic capacity: This price chain is getting stronger from year to year, leading to a global competitive edge for India. This series reflects India’s long-term value creation models for global capacity centres: a mixture of lectures, costs, and digital thinking.
India’s policy structure provides an unmatched edge for any enterprise that wants to take a new look at its operations or expand the global distribution model. The journey of India is based on progressive, digital-supportive, and enterprise-supportive policies until the global capacity centers become the center of global delivery centers. These policy steps, which are supported by dynamic state-level initiatives, have made India a natural option for global companies to build innovation, stability, and platform capabilities.
Inductus GCC as a GCC service provider, sees India not only as a destination but also as a transformative partner. With correct policies, talent, infrastructure, and innovation coordination, India’s GCC ecosystem is ready for the future—laudable, safe, and globally aligned.
GCC is growing fast due to policy support, availability of talent, and economic cost profit. Government policies provide incentives such as fast installation, reduction in compliance costs, and land, infrastructure, and tax exemption. Cities that are emerging (Tier-2 cities) like Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Pune, Chennai, Coimbatore, and Indore are the suitable ones for the GCC. GCC in india is serving in BFSI, Retail, Health Service, Automotive, Fintech, AI and cybersecurity. Yes. Many GCCs innovate with Indian startups through accelerators and sandboxes. Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.
Central Government Policies: Construction of a scalable GCC Ecosystem
Central Policy Initiative
Impact on Global Delivery Centres (GCCs)
Digital India Mission
High-speed digital infrastructure across cities and rural areas enabled remote-first GCC models.
Startup India & Industry-Academia Linkages
Accelerated innovation partnerships between GCCs and Indian deep-tech startups
Ease of Doing Business (Ranked #63 globally)
Reduced regulatory overhead, single-window clearance for global company entry
PLI Schemes (Electronics, IT Hardware)
Encouraged R&D-led GCCs to build and test tech prototypes in India
FDI Liberalisation (100% in IT-BPM)
Made India one of the easiest markets to enter for global firms setting up captives.
India Stack and UPI Ecosystem
Enabled platform-based services innovation across BFSI, retail, and healthcare GCCs
National Skill Development Mission
Created a digitally skilled workforce tailored for GCC 3.0 requirements.
State-level Policy: Local Innovation & Talent Strategy
State
Infra Incentives
Talent & Skilling
Ease-of-Operations Policies
Policy Year
Estimated Investment/Incentive
Karnataka
Beyond Bengaluru IT Policy: Global Innovation Alliance for GCC expansion
AI/ML upskilling via KDEM, CoEs in AI & Cybersecurity
Single-window clearance, R&D grant schemes
2020–2023
₹2,500 Cr+ allocated for tech infra
Telangana
T-Hub, WE Hub, and Tier-2 GCC infra in Warangal & Karimnagar
Telangana Academy for Skill and Knowledge (TASK)—AI/Cloud focus
ICT Policy 2021, flexible labour, and tax incentives
2021–2024
₹1,900 Cr+ across ICT parks and startups
Maharashtra
Fintech and Digital Banking hubs in Mumbai & Pune
NSDC-backed skilling for BFSI and analytics
Stamp duty waivers, plug-and-play co-working infra
2022
₹3,000 Cr fintech cluster in BKC + Pune
Tamil Nadu
New IT parks in Hosur, Coimbatore, and Trichy
TN Skill Development Corp—Semiconductor & AutoTech skilling
Capital subsidies, rental reimbursement for IT space
2021
₹1,400 Cr in Hosur-Coimbatore corridor
Uttar Pradesh
IT Cities in Noida, Greater Noida, and Lucknow with GCC focus zones
Digital skills via UP Skill Development Mission
100% land registration waiver for GCCs in IT sector
2022
₹1,200 Cr in Noida IT hub expansion
Gujarat
GIFT City: India’s first IFSC with fintech sandbox for GCCs
Fintech upskilling, AI & Blockchain startup mentorship
10-year tax holiday in SEZs for tech/GCCs
2020
₹1,800 Cr+ investment in GIFT City Phase 2
Policy Flywheel Effect: From Cost to Capacity
GCC Development in India
Policy to GCC Value Chain
GCC's Policy-Making Future
Conclusion
frequently asked questions (FAQs)

Aditi
Hey, like this? Why not share it with a buddy?
Related Posts
Recent Blog / Post
- Why Mid-Sized Companies are Embracing the GCC Model October 16, 2025
- What Is A Global Capability Center (GCC), and Why Is It Essential For Modern Business? October 16, 2025
- Gurugram’s Tech Ascent: Decoding the New Haryana GCC Policy October 15, 2025
- Scaling Your Tech Team: A Beginner’s Look at the Offshore Development Center October 15, 2025
- Agile Methodologies for GCCs: A Blueprint for Success October 6, 2025
- The Legal and Compliance Checklist for a New GCC Setup October 4, 2025
- The Rise of Niche GCCs: A Focus on Specialised Capabilities October 4, 2025
- The Impact of Regulatory Changes on GCC Operations October 4, 2025
- Cybersecurity for GCCs: A Proactive Approach to Data Protection September 30, 2025
- Beyond Cost: Measuring the True ROI of Your GCC Investment September 29, 2025
- The Future of GCCs in the Retail Sector: A Strategic Playbook September 29, 2025
- David vs Goliath: Mid-Sized GCCs Quietly Outperform the Big Brands September 29, 2025
- Infineon’s Big Bet on India: Inside Its First GCC in GIFT City September 29, 2025
- From Campuses to Capability Centres: How Indian Universities Power the Global GCC Ecosystem September 29, 2025
- Retail Meets Digital: Costco’s GCC in Hyderabad Marks a Global Shift September 29, 2025
















