As the global enterprises are in the race to stay ahead in the hyper-digital era, an important decision often determines the direction of their technical strategy: how should we increase development through outsourcing or by setting up an offshore development center (ODC)?
This question is no longer about cost savings. This innovation is the ownership, talented measurement, and control over intellectual property.
According to Nascom (2025), India now operates more than 55% of global offshore development works. The offshore development model is emerging rapidly as the backbone of long-term digital changes.
Also, IT outsourcing and business process outsourcing (BPO) transactions are continuing to serve firms seeking efficiency. But as technology is becoming a means of strategic development, enterprises are asking, Do we need a seller or a dedicated offshore innovation partner?
In this blog, we clarify the major differences between the IT outsourcing model and the offshore development center, detect cases of real-world use, and help you to choose the right path based on the strategic vision of your organisation.
With the expansion of global enterprises, the demand for scalable, high-quality technical talent and distribution capacity has never been so high before. In 2025, more than 74% of organisations worldwide will report lack of talent as their major technological development barrier.
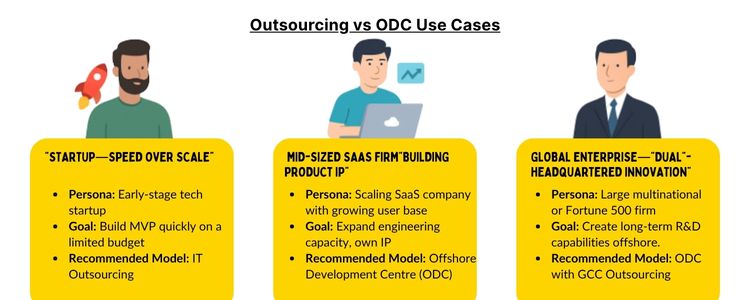
To overcome this problem, there are two models in the global sourcing scenario:
- IT outsourcing (seller-based, working-focused)
- Opportunity Development Centre (ODC) (Owning-based, strategic)
However, many CXOs are confused about these words, resulting in mismatched investment, IP risk, and innovation targets.
frequently asked questions (FAQs)
1.
What is the GCC model of two headquarters?
There is shared leadership and strategic decision-making between the Global Headquarters of the parent company and the GCC in India. This is the GCC model of having two headquarters.
2.
What are the benefits of the model of dual headquarters to Indian GCC?
It transforms Indian GCC as execution units to strategic hubs, and the result is initiatives worldwide, innovation, and attraction of top leadership.
3.
How is GCC aligned on two headquarters, and how is ESG addressed?
Dual-headed buildings enhance the governance, as the local and global leaders regulate the regulatory, ESG and data privacy regulations collaboratively.
4.
Why would the flexi model be alluring to GCC installation?
The Flexi model offers modularized, on-demand services aligning with the fast-changing business needs, particularly the up-and-coming innovation and control and process.
5.
What are the economic advantages of setting up a GCC in India?
India has savings of up to 60 percent, good digital infrastructure, 1.5 million technical graduates, and progressive GCC state-level policies each year.
Aditi
Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.