
Global capability centers (GCC) in India are growing fast. By 2025, India will have over 1,930 GCCs, which will contribute about $64.6 billion to the economy and will give employment to more than 1.9 million professionals. What is behind it? India’s policy emphasises strong digital talent, cost profit, and development of infrastructure. According to Nasscom, more than 500 new GCCs are expected to be established in India by 2030. Companies focus on offshore development services and quick ODC setup in India, but many companies ignore an important column: sustainable GCC infrastructure planning. India’s urban centers – Bangalore to Hyderabad and Pune are being formed by innovative corridors. And in this wave of development, the durable infrastructure is not just good morality; This is a smart business. Let’s analyse long-term GCC infrastructure planning in three horizons. Each stage contains a mixture of environmental, operational, and strategic benefits that are adapted to scalable GCC growth.
Your first infrastructure decisions can affect everything from energy bills to ESG scores. How to do it correctly is mentioned here: Table: Smart Immediate Infrastructure Investments
It is in the midterm plan where the actual changes should start:
This approach not only corresponds to the Net Zero goals of India but also increases retention and operational continuity.
Durability is the strategy here. Long-term GCC for economic growth: think ahead of real estate:
India is not just a GCC region; it is a strategic foundation for large-scale innovation and stability. Global Enterprises are choosing India for long-term GCC development and offshore development services, as reported here: Cost Competitiveness: Government-Backed Basic Infrastructure Speed: Green Policy: Tier-2 Urban Revolution: Workforce and Climate Committee: India offers a powerful mixture of GCC infrastructure readiness, economic benefits, and ESG alignment, which makes it the center of global attraction for the offshore development centers ready for the future.
The infrastructure is no longer limited to buildings; it is becoming a medium for long-term strategy and a significant discrimination in the GCC ecosystem. Leading GCC companies are developing as follows: In the coming years, the service models will emerge—where green, scalable, modular workplaces will be made available with plug-and-play ESG reporting capabilities.
As GCCs become engines of global innovation, the infrastructure will have to develop as an active development promoter from a passive asset. The sustainable infrastructure is no longer optional; this is a strategic requirement for companies investing in GCC setup in India. It increases the ESG score, reduces cost burden, increases flexibility, and ensures long-term business continuity.
India not only provides a place but also provides vision, policy structure, and economic routes to prepare your GCC for the future. Inductus GCC would be a great choice if you are planning to expand offshore development services in India or create a future-safe ODC setup.
Start with energy-skilled retrofitting, smart water and energy metering, provisions of green leases, and basic solar or backup energy systems. Focus on hybrid workplace models, EV preparations, health-operated designs, water recycling, and digital visitor or convenience management systems within 3-5 years. Sustainability and smart campus employees improve welfare, reduce the number of employees, and establish the company as a responsible, future-oriented employer—especially attractive to generation z talents. Yes. Cities like Indore, Bhubaneswar, Coimbatore, and Visakhapatnam provide affordable land, infrastructure encouragement, and low pollution, which are ideal for sustainable ODC setup It improves power reliability, air quality, and digital readiness—which leads to better productivity, uptime, and long-term operational efficiency for offshore development centers. Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.
Horizon 1: Goals: Compliance, Efficiency, and Readiness
Infrastructure Area
Sustainable Solution
ROI Period
Cost Impact
Lighting
LED systems with dynamical movements
6–12 months
Saving of 20 – 25 percent energy
Cooling
VRF HVAC systems
1–2 years
30% less power consumption
Water
Smart flow and recycling
1 year
40% less use of water
Backup Energy
Solar battery systems
2 years
Green power continuity
Horizon 2: Target: Hybrid Work, Smart Design, and Employee Welfare
Horizon 3: Target: Flexibility, Innovation, and Net-Zero
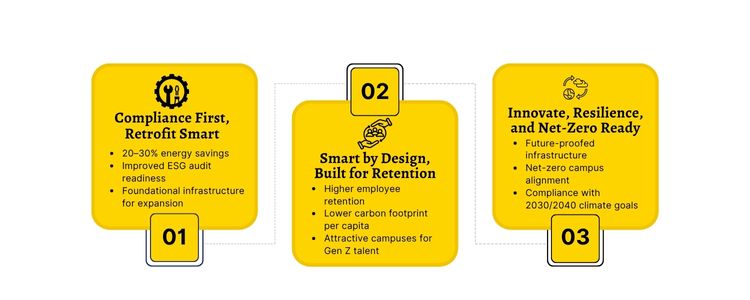
India's Economic and Environmental Benefits
Infrastructure Strategy for GCC Leaders
Conclusion
frequently asked questions (FAQs)

Aditi
Hey, like this? Why not share it with a buddy?
Related Posts
Recent Blog / Post
- Pharma GCC Setup Services in India: Strategic Considerations for CXOs January 9, 2026
- Why Enterprises Are Rethinking Their GCC Strategies in 2026 January 8, 2026
- Why Most Enterprise Expansion Strategies Fall Short of Projections, And How a GCC Enabler Can Bridge the Gap January 7, 2026
- India’s GCC Ecosystem: Why the World’s Biggest Companies Are Betting Their Future on it January 3, 2026
- Healthcare GCCs in India: Where the World’s Pharmaceutical Innovation Actually Happens January 2, 2026
- Circular Economy Models and Their Relevance to Manufacturing GCCs December 30, 2025
- GCCs in Agritech: Digitizing Global Food Security December 29, 2025
- Renewable Energy GCCs: Accelerating Global Green-Tech Development December 29, 2025
- Cyber Resilience 2030: Multi-Layer Security Architecture for GCCs December 26, 2025
- Building an Integrated Risk Management Framework for Multi-Region GCCs December 26, 2025
- The Ethics of Automation: How GCCs Maintain Human Oversight in AI Workflows December 25, 2025
- Future of HR in GCCs: Data-Led, Skills-Based, and GenAI-Driven December 25, 2025
- The Proposal to Standardize India’s GCCs for Unshakeable Global Leadership December 24, 2025
- Global Capability Centers: A Strategic Growth Model for B2B Enterprises December 24, 2025
- AI Ethics & Compliance Mandates for GCC Operations in 2025 December 23, 2025















