
The Global Capability Centre (GCC) has gone beyond the back-office support function. Today, they are powerful engines of innovation, digital changes, and commercial agility for global enterprises. A major strength that pursues this change is the rise of data science hubs within the GCC. As data is becoming the centre of business strategy, enterprises are turning to their India-based GCC to build advanced analytics and AI capabilities that facilitate real-time insight, automation, and better decision-making. India is a pioneer in the matter with its huge talent pool and tech ecosystem. According to Nasscom, more than 45% of the global GCC is a data and analytics COE (Centre of Excellence) located in India, and this number is expected to increase. As a leading GCC service provider in India, we see the data science hub as an important part of the gcc operating model prepared for the future. India has emerged as a favourite destination for the establishment of these hubs. More than 1800 GCCs are in the country, and these centres are working with more than 2 million professionals. India contributes significantly to global digital change efforts. About 70% of the top 500 companies with GCC in India have established analytics or AI excellence centres, confirming the important value of data science. This blog explains how the data science hub gives strength to GCC operating models and why India is leading this change.
Data Science Hub is a special unit within a GCC that brings together data scientists, engineers, analysts, and AI/ML experts to solve business problems by using data. These hubs go beyond traditional BI (Business Intelligence) and dashboards. They focus on this: These hubs serve many commercial units globally and help to provide faster, smarter, and more cost-effective solutions.
Modern GCC is not just a support centre; It is a strategic global innovation centre. Here, it is described how the data science hub adds value to the GCC operating model:
India offers a unique mixture of cost profit, intensive technical expertise, and a prosperous digital ecosystem, which creates a global epicentre for data science centres. Here is described why global companies like India: As a result, India is no longer only a low-cost distribution centre but has developed as a strategic analytics and innovation partner for the global captive centres.
Here are some real examples that show how global companies are changing operations through India-based data science hubs: These examples reflect how data science hubs can be deeply embedded into enterprise functions, solving complex challenges across industries.
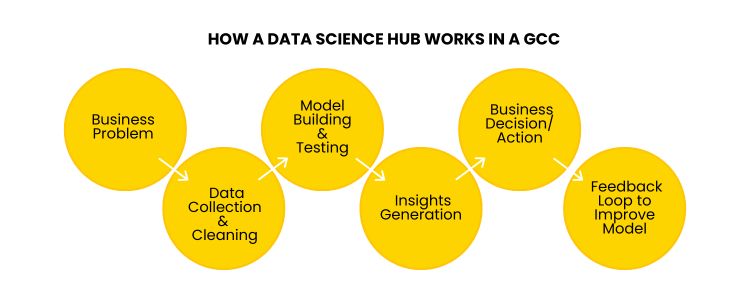
Normal workflow of the data science hub in GCC follows a structured, recurring process: Step 1: Identification of business problem – Collaborate with business stakeholders to define clear objectives and KPIs. Step 2: Data acquisition and preparation – Collect relevant data from different sources and clean it for analysis. Step 3: Model construction and verification – Develop machine learning models, test various algorithms, and validate the performance. Step 4: Insight Building – Translate the model output into actionable insights for those who decide. Step 5: Model perineogen – Integrate the model into commercial workflow using API or dashboard. Step 6: Reaction and Adaptation – Monitor the performance of the real world and continuously refine the model.
While data science centres provide significant potential, organisations often face obstacles in increasing their effectiveness due to:
To assess the success and maturity of the data science hub, businesses must track a set of defined KPIs that measure accuracy, adoption, professional impact, and innovation speed. Here is a detailed outline: These metrics help ensure the data science hub evolves from a cost center to a core value generator for the enterprise.
The future of data science centres in the GCC is taking shape by many successful trends: In the coming years, GCC will develop as a fully developed AI and innovation centre in which data science businesses will be at the centre of strategy.
In today’s data-first world, the Data Science Centre is no longer an alternative. They are at the centre of how to operate business change by modern GCC. India, with its vibrant talent and intensive expertise, is an ideal place to build these next-generation capabilities.
As a reliable GCC service provider in India, Inductus GCC understands that today businesses need more than talent; They need strategic insights, scalable platforms, and AI-ready infrastructure. We specialise in helping global enterprises to establish and enhance the highly affected data science centres within their GCC. Whether you are starting your analytics trip or moving towards AI maturity, we offer people, procedures, and platforms to make it possible.
A centralised team within the GCC focuses on solving business problems using AI, ML and Analytics. India offers a strong talent pool, cost efficiency, and a strong digital infrastructure. Model accuracy, business effects, time-to-time, peripiny frequency, and recurrence. Python, R, Tensorflow, Spark, Power BI, Azure, AWS, etc. It helps to create an insight, to automate material construction, and support advanced decision making. Aditi, with a strong background in forensic science and biotechnology, brings an innovative scientific perspective to her work. Her expertise spans research, analytics, and strategic advisory in consulting and GCC environments. She has published numerous research papers and articles. A versatile writer in both technical and creative domains, Aditi excels at translating complex subjects into compelling insights. Which she aligns seamlessly with consulting, advisory domain, and GCC operations. Her ability to bridge science, business, and storytelling positions her as a strategic thinker who can drive data-informed decision-making.
What are Data Science Hubs?
How Data Science Improves the GCC Operating Model!!
GCC in India: Ideal Data Science Hubs
Real Case of Use of Data Science Hub
How Data Science Hub Works in GCC!!
Challenges in Integrating Data Science in GCC
Measurement Framework: How to Evaluate Data Science Hub
Metric
Description
Why It Matters
Model Accuracy
Measures how well the model’s predictions align with actual outcomes
Ensures the model’s reliability and credibility
Business Impact
Quantifies revenue growth, cost savings, or risk reductions achieved through data science efforts
Links analytics to tangible financial or operational outcomes
Time-to-Insight
Duration from data ingestion to actionable business insights
Reflects agility in decision-making and responsiveness to market changes
Model Deployment Frequency
Number of models moved to production within a time frame
Indicates operational maturity and ability to scale innovations
Model Reusability
Percentage of models or components reused across
Enhances ROI by maximizing utility of developed assets
Stakeholder Adoption Rate
Percentage of intended business users actively using data science solutions
Demonstrates organizational buy-in and relevance of analytics
Return on Investment (ROI)
Total financial return from data science initiatives relative to the investment made
Measures overall value delivery of the data science hub
Innovation Velocity
Number of new projects, prototypes, or pilots launched quarterly
Captures the pace of experimentation and strategic innovation
Data Pipeline Reliability
Frequency and duration of data pipeline outages or issues
Indicates data infrastructure robustness and model performance consistency
Time-to-Deploy
Average time taken to move a model from experimentation to production
Tracks process efficiency and collaboration between data science and engineering teams
Future Approach: GenAI and Next Gen Data Science
Conclusion
frequently asked questions (FAQs)

Aditi
Hey, like this? Why not share it with a buddy?
Related Posts
Recent Blog / Post
- The Green GCC Framework: Carbon Neutral by Design December 11, 2025
- Data Residency, Privacy, and Global Governance Challenges in GCCs December 11, 2025
- Applying Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) for Next-Gen GCC Cost Optimisation. December 10, 2025
- The Silent Crisis: Strategic Plays for Captive Centers to Avoid the ‘Year Three Plateau’ December 10, 2025
- Why Emotional Intelligence Is a Must-Have Competency in GCC Leaders December 10, 2025
- Bridging the Trust Gap: Unlocking European GCC Potential in India December 10, 2025
- The Telecom GCC Innovation Centre’s Role in Global 5G/6G Network Virtualisation. December 8, 2025
- Managing ITAR and Export Controls: The High-Security Mandate for Defence Captive Centers December 8, 2025
- Policy and the Multi-City GCC Grid: Catalyzing India’s Next Wave of Global Capability December 6, 2025
- BFSI GCC Digital Transformation: Moving from Back Office to Front-Line FinTech Innovation. December 6, 2025
- Pharma Global Capability Centers: Accelerating Drug Discovery with Computational Chemistry December 6, 2025
- ‘Capability’ and ‘Sustainability’ as the New Twin Drivers of GCC 3.0 December 4, 2025
- Beyond Cost: Using Value-Per-Employee (VPE) as the New Metric for GCC Cost Optimisation. December 3, 2025
- From Cost Arbitrage to Global Chip Architect: Securing India’s Tech Future December 2, 2025
- The Great Reskilling Challenge: Preparing the Workforce for GCC Digital Transformation by 2025 December 2, 2025
















